A) pressure on nominal wages to fall and this shifts the SRAS curve rightward.
B) pressure on nominal wages to rise and this shifts the SRAS curve rightward.
C) pressure on nominal wages to fall and this shifts the SRAS curve leftward.
D) pressure on nominal wages to rise and this shifts the SRAS curve leftward.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-3 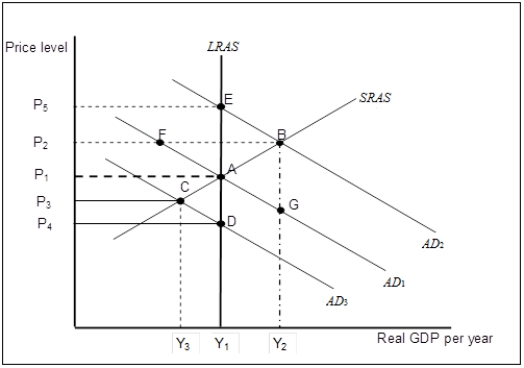 -Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth. In the short-run,
-Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth. In the short-run,
A) the nominal wage rate falls.
B) unemployment is above its natural level.
C) there will be pressure on prices to rise.
D) the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left as firms cut production.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 7-1
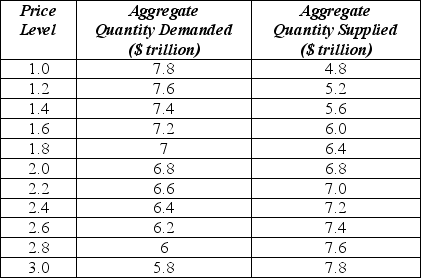 Table 7-1 shows the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves for an economy. The potential level of output is $7.6 trillion.
-Refer to Table 7-1. If policymakers choose to close the gap by using stabilization policy, they should use
Table 7-1 shows the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves for an economy. The potential level of output is $7.6 trillion.
-Refer to Table 7-1. If policymakers choose to close the gap by using stabilization policy, they should use
A) contractionary fiscal or monetary policies.
B) expansionary fiscal or monetary policies.
C) a combination of contractionary fiscal and expansionary monetary policies.
D) a combination of expansionary fiscal and contractionary monetary policies.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, predict what happens in the short run when the federal government lowers the capital gains tax to stimulate investment.
A) The aggregate demand curve shifts left; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP decrease.
B) The aggregate demand curve shifts right; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP increase.
C) The aggregate supply curve shifts left; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level increases; real GDP decreases.
D) The aggregate supply curve shifts right; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level decreases; real GDP increases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The intersection of the economy's aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply curves I. determines its equilibrium real GDP in both the long run and the short run. II. determines its equilibrium price level in both the long run and the short run. III. occurs at the economy's potential output.
A) I, II, and III
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) III only
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve
A) relates the level of nominal output produced by firms to the implicit price deflator.
B) relates the level of output produced by firms to the price level in the long run.
C) is vertical because there is one price level and an infinite number of outputs.
D) is determined by the real output demanded by economic agents in an economy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is false about potential output?
A) It is the level of output an economy can achieve when labor is employed at its natural level.
B) It is the long run output level that guarantees price stability.
C) It is also called the natural level of real GDP.
D) If a country is producing its potential output, then it is producing at a point on its production possibilities frontier.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at
A) potential output.
B) the actual level of real output.
C) the actual level of nominal output.
D) 100% employment of the labor force.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward because of
A) wage and price stickiness.
B) wage and price flexibility.
C) increasing technology.
D) a reduction in resource availability at higher price levels.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-7 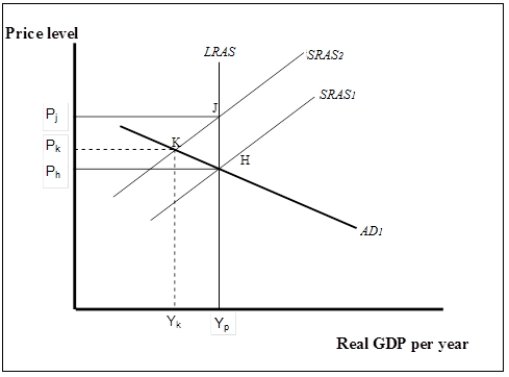 -Refer to Figure 7-7. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at point K. If the policy-makers adopt a nonintervention policy, over time,
I. real wages will fall as long as unemployment remains above the natural rate.
II. lower nominal wages will result in a gradual shift from SRAS2 to SRAS1.
III. long-run equilibrium will be established at YP and Ph.
-Refer to Figure 7-7. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at point K. If the policy-makers adopt a nonintervention policy, over time,
I. real wages will fall as long as unemployment remains above the natural rate.
II. lower nominal wages will result in a gradual shift from SRAS2 to SRAS1.
III. long-run equilibrium will be established at YP and Ph.
A) I, II, and III
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) III only
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in aggregate demand, all other things unchanged, in the long run will generate
A) an increase in potential output and no change in the price level.
B) a decrease in potential output and no change in the price level.
C) no change in potential output and an increase in the price level.
D) no change in potential output and a decrease in the price level.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium. Which of the following events leads to an increase in the price level and real GDP in the short run?
A) A decrease in health insurance premiums paid by firms raises the cost of employing labor
B) An increase in government transfer payments
C) An increase in the cost of a key input such as oil
D) A sharp fall in stock market prices
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs if an economy experiences an inflationary gap? I. Actual real GDP is less than potential output. II. Actual real GDP is greater than potential output. III. Unemployment is less than the natural rate. IV. Unemployment is greater than the natural rate.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the short run, all prices are flexible.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If an economy is operating at its potential output level, a change in aggregate demand or short-run aggregate supply will induce an inflationary or a recessionary gap.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-3  -Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose net exports increase. What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
-Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose net exports increase. What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
A) The economy will return to its initial equilibrium at point A.
B) Equilibrium will be re-established at point B with a higher potential output.
C) Equilibrium will be re-established at point E at a higher price level.
D) The aggregate demand curve will shift back to AD1.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-7  -Refer to Figure 7-7. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at K. Policy makers could either pursue a stabilization policy or allow the economy to adjust on its own. What is the difference between the two policy choices, if any?
-Refer to Figure 7-7. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at K. Policy makers could either pursue a stabilization policy or allow the economy to adjust on its own. What is the difference between the two policy choices, if any?
A) Both policies would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pj.
B) Both policies would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Ph.
C) A stabilization policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pj while a nonintervention policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Ph.
D) A stabilization policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Ph while a nonintervention policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pj.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-6 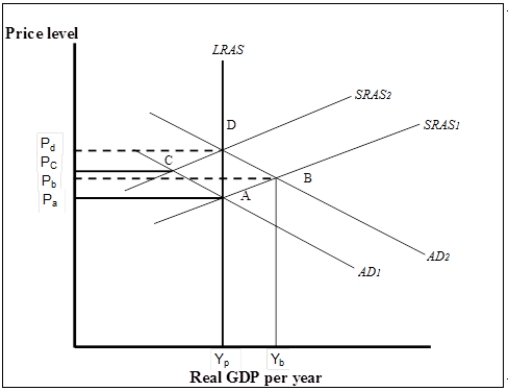 -Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. If policy-makers decide to intervene to close the gap, which of the following can it do?
-Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. If policy-makers decide to intervene to close the gap, which of the following can it do?
A) Decrease personal income taxes.
B) Increase government welfare spending.
C) Decrease the level of government purchases of goods and services.
D) Institute investment tax credits to encourage business investment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in the aggregate quantities of goods and services demanded at each price level is called a
A) change in aggregate demand.
B) change in the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded.
C) determinant of aggregate demand.
D) revealed expenditure on aggregate demand.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-1 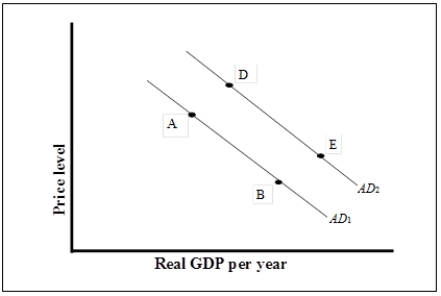 -Refer to Figure 7-1. A movement from point A to point B
-Refer to Figure 7-1. A movement from point A to point B
A) is a change in aggregate demand resulting from a lower price level.
B) is a change in aggregate quantity demanded resulting from a lower price level.
C) could be due to an increase in investment demand.
D) occurs because aggregate output supplied has increased.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 166
Related Exams