A) organelles derived from neighboring cells.
B) highly derived mitochondria that can also provide ATP.
C) extensions of the Golgi apparatus.
D) vesicles budded off from rough ER that do not fuse with the Golgi apparatus.
E) modifications of smooth ER within the muscle cells.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
In the process of centrifuging a cell homogenate in a centrifuge tube,the cell structures are separated according to size and _______.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Certain cells in your pancreas make digestive enzymes that are secreted into ducts and carried to your small intestine.If you looked at these pancreatic cells by electron microscopy,you would expect to see
A) large amounts of rough ER.
B) multiple nuclei per cell.
C) large numbers of primary lysosomes.
D) numerous cilia on the cell surfaces.
E) few ribosomes but numerous vacuoles.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a plant cell,the genes that code for all the proteins found in a chloroplast are located in the
A) nucleus.
B) nucleiod.
C) DNA of the chloroplast.
D) thylakoids.
E) nuclear and chloroplast DNA.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below showing a time-lapse series of vesicles being moved along a cytoskeletal structure in the direction of the arrow.The minus (‒) and plus (+) ends of the cytoskeletal structure are indicated.The most likely explanation for the movement of the vesicles is that they are being moved along a(n) _______ by _______. 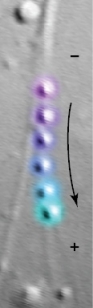
A) intermediate filament such as a hair;the flowing movement of the cytoplasm
B) microfilament;cytoplasmic streaming
C) actin microfilament;a motor protein such as myosin
D) microtubule;a motor protein such as kinesin
E) microtubule;a motor protein such as dynein
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows structures found in a(n) _______.The structures labeled 1,2 and 3 represent _______,_______ and _______,in that order. 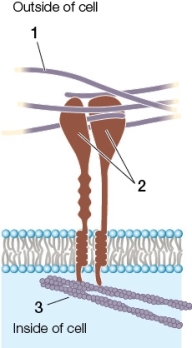
A) animal;extracellular fibers;integrin;actin
B) animal;extracellular fibers;kinesin;microfilaments
C) plant;cellulose;plasmodesmata;ribosomes
D) plant;polysaccharides;cross-linked proteins;peroxisomes
E) bacterium;the peptidoglycan layer;linker-proteins;the cytoskeleton
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane
A) increase the volume of the mitochondrial matrix.
B) decrease the surface-to-volume ratio of the mitochondrion.
C) create a large membrane surface for reactions within the mitochondrion.
D) increase the number of ribosomes within the membrane.
E) enclose the mitochondrial DNA in a double membrane.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mitochondria and chloroplasts differ in that
A) mitochondria contain DNA,but chloroplasts do not.
B) chloroplasts contain DNA,but mitochondria do not.
C) mitochondria harvest chemical energy,whereas chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy.
D) mitochondria are enclosed within one membrane,whereas chloroplasts are enclosed within two.
E) mitochondria have extensive infoldings of membrane,whereas chloroplasts do not have extensive internal membranes.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents is the correct arrangement of items in order of size,from smallest to largest?
A) Lipid molecule;carbon atom;bacterium;virus;plant cell
B) Bacterium;virus;carbon atom;lipid molecule;plant cell
C) Carbon atom;lipid molecule;virus;bacterium;plant cell
D) Plant cell;bacterium;virus;carbon atom;lipid molecule
E) Carbon atom;lipid molecule;bacterium;virus;plant cell
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a living cell grows larger,in what ways do its metabolic processes change?
A) Its need for resources increases.
B) Its rate of waste production decreases.
C) Movement of substances within the cell becomes faster.
D) The amount of surface area needed to support its metabolic processes decreases.
E) Its needs for nutrients decreases.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ribosomes are the structures in which
A) chemical energy is stored in the form of ATP.
B) cell division is controlled.
C) genetic information is used to make proteins.
D) sunlight energy is converted into chemical energy.
E) new organelles are made.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which molecule will cross a cell membrane most easily?
A) A large molecule such as hemoglobin
B) A small molecule such as glucose
C) Genetic material such as DNA
D) A highly polar molecule such as water
E) A lipid-soluble substance such as testosterone
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the inner membrane of a mitochondrion were not folded to create cristae,
A) the mitochondrion would not be able to make as much ATP.
B) the outer membrane would become as permeable to macromolecules as the inner membrane is.
C) the production of glucose within the mitochondrion would decrease.
D) the mitochondrion would not be as efficient at using solar energy to make ATP.
E) the mitochondrion would not be able to maintain its shape.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All cellular membranes
A) regulate which materials can cross the membrane.
B) support the cell and determine its shape.
C) produce energy for the cell.
D) produce proteins for the cell.
E) move the cell.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mitochondria,the energy from "food" molecules (such as glucose) that is partially broken down in the cytosol is converted to
A) ATP.
B) CTP.
C) GTP.
D) TTP.
E) UTP.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions :
Refer to the figure below. 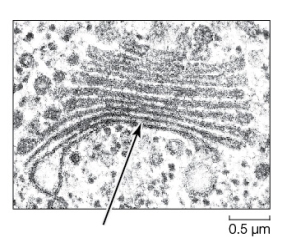 -The electron micrograph shows a portion of a cell.This cell could have come from
-The electron micrograph shows a portion of a cell.This cell could have come from
A) a bacterium,but not a protist.
B) an archaeon,but not a bacterium.
C) a plant,but not an animal.
D) a plant or animal,but not a bacterium.
E) an animal,but not a plant.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you wanted to stain the ribosomes in a cell,you could use a dye that stains
A) carbohydrates.
B) nucleic acids.
C) fatty acids.
D) basic (as opposed to acidic) components.
E) phospholipids.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell needed to increase its surface area without changing its volume in order to carry out cellular processes more efficiently,it could do this most effectively
A) by creating deep invaginations in the cell membrane.
B) by becoming spherical in shape.
C) by becoming flatter.
D) by becoming columnar-shaped (tall and narrow) .
E) It is impossible for a cell to increase its surface area without changing its volume.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major distinction between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell?
A) The DNA in a prokaryotic cell is not separated from the ribosomes.
B) A prokaryotic cell does not have RNA.
C) A prokaryotic cell is larger than a eukaryotic cell.
D) Prokaryotic cells can build tissues but not organs.
E) A prokaryotic cell is functionally simpler than a eukaryotic cell and its biochemical reactions occur more slowly.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most cells are small because
A) a reduced surface area-to-volume ratio increases metabolic rates within the cell.
B) a larger surface area-to-volume ratio increases the efficiency of processes within the cell.
C) small cells are able to live longer than large cells.
D) small cells lose less heat to the environment than large cells.
E) it is easier to package small cells within a cell wall.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 115
Related Exams