A) functional; nonfunctional
B) complementing; competing
C) virulent; avirulent
D) former; nonformer
E) lytic; lysogenic
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a mixed infection experiment,the results of an h+r and hr+ cross are as follows. 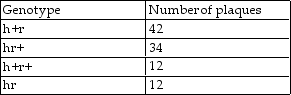 How far apart are these two genes?
How far apart are these two genes?
A) 12
B) 24
C) 48
D) 8
E) 2
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that one counted 67 plaques on a bacterial plate where 0.1 ml of a 10-5 dilution of phage was added to bacterial culture.What is the initial concentration of the undiluted phage?
A) 6.7 × 10-5 pfu/ml
B) 0.1 × 105 pfu/ml
C) 6.7 × 105 pfu/ml
D) 67 pfu/ml
E) 6.7 × 107 pfu/ml pfu = plaque- forming units
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A form of bacterial recombination that involves a viral intermediate is called ______.
A) plaque assay
B) transduction
C) transformation
D) conjugation
E) competency
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bacteria that are in a particular physiological state to become transformed are called______ .
A) resistant
B) episomal
C) transformable
D) temperate
E) competent
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Name two forms of recombination in bacteria.
A) auxotrophic and prototrophic
B) conjugation and transduction
C) lytic and lysogenic
D) insertion and replication
E) mixed and generalized
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
______have lost,through ______,the ability to grow on minimal medium.
A) prototrophs; adaptation
B) mutants; adaptation
C) prototrophs; mutation
D) auxotrophs; mutation
E) auxotrophs; adaptation
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Name the general category into which double- stranded circular extrachromosomal DNA elements such as F factors,ColE1,and R would fall.
A) r- determinant
B) plaque
C) partial diploid
D) capsid
E) plasmid
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
______can exist integrated into the bacterial chromosome or as an autonomous plasmid unit in the cytosol.
A) Col plasmid
B) Temperate phages
C) Episomes
D) F' plasmid
E) R factor
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an episome?
A) F factor and temperate phage
B) lytic phage
C) F factor
D) temperate and lytic phages
E) temperate phage
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do different strains of E.coli can reveal different linkage arrangements of genes in Hfr crosses?
A) They do not.All Hfr strains are identical.
B) Different strains may have different F factors and therefore different initiation points for chromosome transfer.
C) Hfr strains will demonstrate different areas of recombination,due to dominance and recessiveness of genes.
D) In different Hfr strains,different genes will be transferred based on where the centromere resides.
E) In different Hfr strains,genes can be in different order on the chromosome.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the adaptation hypothesis?
A) The bacteria will mutate so it can become an auxotroph.
B) The phage mutates to infect bacteria more effectively.
C) The phage mutates so it can't infect bacteria any longer.
D) The phage and bacteria both mutate so the phage becomes less virulent.
E) The phage stimulates the bacteria to mutate to become immune to the phage.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the first step in phage formation inside the bacterial cell?
A) tail formation
B) tail fibers are added
C) DNA packaging as the viral heads assemble
D) adherence to the pilus
E) lysis
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs during cell lysis?
A) prophage formation
B) plaque formation
C) lysogeny
D) binary fission
E) episome propagation
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bacteriophage that is capable of entering either a lytic or a lysogenic cycle is called an______.
A) temperate bacteriophage
B) virulent bacteriophage
C) plasmid
D) plaque- forming unit
E) episome
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the process by which a temperate bacteriophage infects a bacterial cell and subsequently integrates its chromosome into the bacterial chromosome?
A) lysogeny
B) transduction
C) temperate
D) transformation
E) lysis
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a bacteriophage?
A) a bacterium that infects other bacteria
B) a bacterium that infects a virus
C) a virus that exclusively undergoes the lytic cycle
D) a virus that exclusively undergoes the lysogenic cycle
E) a virus that has a bacterium as its host
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a mixed infection experiment,you study two plaque phenotypes of large l+ versus small l- and bumpy b+ versus smooth b- .You mix small l- b+ with smooth l+ b- and identify 50 small,smooth and 47 large,bumpy.How far apart are the genes?
A) 490
B) 99
C) 49
D) 1000
E) There is not enough information to calculate the distance.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false?
A) A symbiotic relationship between a phage and a bacterium apparently occurs in the process of lysogeny.
B) Lysogeny is a process that occurs during transformation and conjugation.
C) A bacteriophage that can only undergo lysis is called a virulent phage.
D) A prophage can exist in a quiescent state in the bacterial chromosome.
E) Viral genomes comprise only genes for viral structure and assembly.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transduction is a form of recombination in bacteria that involves______ .
A) fertility factors
B) physical contact between the bacteria involved
C) plasmids
D) 5- bromouracil
E) bacteriophages
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 49
Related Exams