A) the apex of the heart hitting the anterior chest wall.
B) a stenotic atrioventricular valve.
C) the large force of the contracting ventricles.
D) vibrations that result from the semilunar valves slamming shut.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pericarditis can lead to all of the following except
A) excess fluid in the pericardial cavity.
B) pericardial friction rub.
C) adhesions.
D) a myocardial infarction.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Contraction of the ventricles begins at the apex and proceeds superiorly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The right ventricle pumps blood into the
A) aorta.
B) pulmonary vein.
C) pulmonary trunk.
D) superior vena cava.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Heart valve with two cusps.
A) mitral
B) pulmonary semilunar
C) aortic semilunar
D) fossa ovalis
E) crista terminalis
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
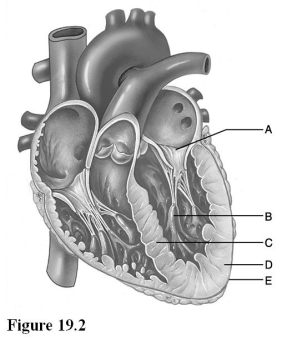 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the location of the bundle branches.
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the location of the bundle branches.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Irregular ridges in the walls of the ventricles are called ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
The ________ valve prevents backflow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium.
Correct Answer

verified
mitral, le...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
The first part of the heart sound "lub-dup" is produced by the closing of the right and left ________.
Correct Answer

verified
atrioventr...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
The ________ artery supplies the left atrium and the posterior part of the left ventricle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
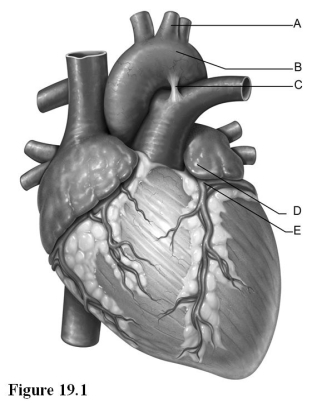 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the left coronary artery.
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the left coronary artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ returns most of the venous blood from the heart to the right atrium.
A) great cardiac vein
B) coronary sinus
C) anterior cardiac vein
D) posterior interventricular vein
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blood in the pulmonary veins returns to the
A) right atrium.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) left ventricle.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the ligamentum arteriosum.
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the ligamentum arteriosum.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The parasympathetic fibers of the vagus nerve
A) speed up the heartbeat.
B) increase the force of cardiac contractions.
C) slow the heartbeat.
D) decrease the force of cardiac contractions.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Uncoordinated contractions of the ventricle, known as ________, result from irregularities in conducting system behavior.
Correct Answer

verified
fibrillation
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Parasympathetic fibers innervate the SA node, AV node, and cardiac musculature.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crista terminalis can be used to locate all of the following structures except the
A) opening of the coronary sinus.
B) opening of the inferior vena cava.
C) opening of the pulmonary veins.
D) opening of the superior vena cava.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A penetrating stab wound to the heart wall that causes blood to leak into the pericardial cavity would result in
A) cardiac tamponade.
B) myocardial infarction.
C) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
D) endocarditis.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures is not found in the left ventricle?
A) pectinate muscles
B) mitral valve
C) trabeculae carneae
D) papillary muscles
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 114
Related Exams