A) J/C
B) V/C
C) J2/C
D) C/J
E) C2/J
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capacitors A and B are identical.Capacitor A is charged so it stores 4 J of energy and capacitor B is uncharged.The capacitors are then connected in parallel.The total stored energy in the capacitors is now:
A) 16 J
B) 8 J
C) 4 J
D) 2 J
E) 1 J
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capacitor C1 is connected alone to a battery and charged until the magnitude of the charge on each plate is 4.0 * 10-8 C.Then it is removed from the battery and connected to two other capacitors C2 and C3, as shown.The charge on the positive plate of C1 is then 1.0 * 10-8 C.The charges on the positive plates of C2 and C3 are: 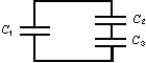
A) q2 = 3.0 *0 10 - -8 C and q3 = 3.0 *10 - 8 C
B) q2 = 2.0 *10 - 8 C and q3 = 2.0 *10 - 8 C
C) q2 = 5.0 *10 - 8 C and q3 = 1.0 *10 - 8 C
D) q2 = 3.0 * 10 - 8 C and q3 = 1.0 *10 - 8 C
E) q2 = 1.0 * 10 - 8 C and q3 = 3.0 *10 - 8 C
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2- F and a 1- F capacitor are connected in series and charged from a battery.They store charges P and Q, respectively.When disconnected and charged separately using the same battery, they have charges R and S, respectively.Then:
A) R > S > Q = P
B) P > Q > R = S
C) R > P = Q > S
D) R = P > S = Q
E) R > P > S = Q
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference between a polar dielectric and a nonpolar dielectric?
A) A polar dielectric has a permanent electric field.
B) A nonpolar dielectric never has an internal electric field.
C) The molecules of a polar dielectric have a permanent electric dipole moment.
D) A nonpolar dielectric can have an induced electric field in any direction.
E) A polar dielectric is always aligned with the Earth's electric field.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capacitors C1 and C2 are connected in series and a potential difference is applied to the combination.If the capacitor that is equivalent to the combination has the same potential difference, then the charge on the equivalent capacitor is the same as:
A) the charge on C1
B) the sum of the charges on C1 and C2
C) the difference of the charges on C1 and C2
D) the product of the charges on C1 and C2
E) none of the above
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Let Q denote charge, V denote potential difference and U denote stored energy.Of these quantities, capacitors in parallel must have the same:
A) Q only
B) V only
C) U only
D) Q and U only
E) V and U only
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is:
A) proportional to the plate area
B) proportional to the charge stored
C) independent of any material inserted between the plates
D) proportional to the potential difference of the plates
E) proportional to the plate separation
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A charged capacitor stores 10 C at 40 V.Its stored energy is:
A) 400 J
B) 200 J
C) 4 J
D) 2.5 J
E) 1.25 J
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the plate separation of an isolated charged parallel-plate capacitor is doubled:
A) the electric field is doubled
B) the potential difference is halved
C) the charge on each plate is halved
D) the surface charge density on each plate is doubled
E) none of the above
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If both the plate area and the plate separation of a parallel-plate capacitor are doubled, the capacitance is:
A) doubled
B) halved
C) unchanged
D) one-fourth the original
E) quadrupled
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the plate area of an isolated charged parallel-plate capacitor is doubled:
A) the electric field is doubled
B) the potential difference is halved
C) the charge on each plate is halved
D) the surface charge density on each plate is doubled
E) none of the above
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2- F and a 1- F capacitor are connected in series and a potential difference is applied across the combination.The 2- F capacitor has:
A) twice the charge of the 1- F capacitor
B) half the charge of the 1- F capacitor
C) twice the potential difference of the 1- F capacitor
D) half the potential difference of the 1- F capacitor
E) none of the above
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two parallel-plate capacitors with different plate separation but the same capacitance are connected in series to a battery.Both capacitors are filled with air.The quantity that is NOT the same for both capacitors when they are fully charged is:
A) potential difference
B) stored energy
C) electric field between the plates
D) charge on the positive plate
E) dielectric constant
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two capacitors are identical except that one is filled with air and the other with oil.Both capacitors carry the same charge.The ratio of the electric fields Eair/Eoil is:
A) between 0 and 1
B) 0
C) 1
D) between 1 and infinity
E) infinite
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A parallel-plate capacitor has a plate area of 0.2 m2 and a plate separation of 0.1 mm.To obtain an electric field of 2.0 *106 V/m between the plates, the magnitude of the charge on each plate should be:
A) 3.5 * 10-6 C
B) 7.1 *10-6 C
C) 1.4 * 10-5 C
D) 1.8 * 10-5 C
E) 8.9 * 10-5 C
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An air-filled capacitor is charged, and then a dielectric is inserted.As a result, there is an induced charge on the dielectric.What is the difference between induced charge and free charge?
A) There is no difference.
B) Induced charge does not result in a net charge on the dielectric.
C) Induced charge is smaller than free charge.
D) Free charge creates an electric field, but induced charge does not.
E) Free charge creates an electric potential, but induced charge does not.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each plate of a capacitor stores a charge of magnitude 1 mC when a 100-V potential difference is applied.The capacitance is:
A) 5 F
B) 10 F
C) 50 F
D) 100 F
E) none of these
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 20-µF capacitor is charged to 200 V.Its stored energy is:
A) 4000 J
B) 4 J
C) 0.4 J
D) 0.1 J
E) 0.004 J
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 59 of 59
Related Exams