A) substrate level phosphorylation.
B) gain of an oxygen atom and its electrons.
C) loss of an electron.
D) a dehydrogenation event.
E) loss of hydrogen atom.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a non- protein carrier found in some electron transport chains?
A) ribozymes
B) metal- containing proteins
C) flavoproteins
D) ubiquinones
E) cytochromes
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning reduction reactions is FALSE?
A) A molecule gains a hydrogen atom.
B) An electron acceptor becomes more positively charged.
C) An electron acceptor gains an electron.
D) They are coupled with oxidation reactions.
E) They frequently involve electron carrier molecules.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a fermentation product useful in the manufacture of cheese?
A) acetic acid
B) ammonia
C) pyruvic acid
D) lactic acid
E) ethanol
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
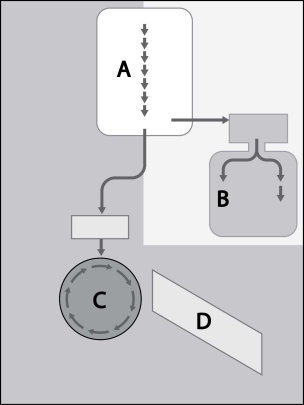 Identify the processes of glucose metabolism represented in Figure 5- 1.
Identify the processes of glucose metabolism represented in Figure 5- 1.
A) A = glycolysis, B = fermentation, C = Krebs cycle, D = electron transport chain.
B) A = glycolysis, B = Krebs cycle, C = fermentation, D = electron transport chain
C) A = fermentation, B = glycolysis, C = Krebs cycle, D = electron transport chain
D) A = glycolysis, B = Krebs cycle, C = electron transport chain, D = fermentation.
E) A = electron transport chain, B = Krebs cycle, C = glycolysis, D = fermentation
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is TRUE concerning the structure and function of enzymes?
A) Enzymes can function at a wide range of pH.
B) Competitive inhibition of an enzyme occurs when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme.
C) An apoenzyme is a combination of a cofactor bound to a holoenzyme.
D) All enzymes bind cofactors necessary for their function.
E) After an enzyme has catalyzed a reaction, it resumes its original shape and can interact with a new substrate molecule.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
During glycolysis, glucose is converted to (pyruvic/acetic/lactic) acid, a molecule that can be used in either fermentation or respiration pathways.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Laboratory fermentation tests often include a pH indicator because many bacteria produce (CO2/bases/acids) as they ferment carbohydrates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Significant amounts of the NADPH required for the Calvin- Benson cycle are produced during the (cyclic/noncyclic) photophosphorylation reactions of photosynthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following produces NADPH?
A) the Entner- Doudoroff pathway only
B) the pentose phosphate pathway only
C) the Embden- Meyerhof pathway only
D) both the Embden- Meyerhof and Entner- Doudoroff pathways
E) both the pentose phosphate and Entner- Doudoroff pathways
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Reactions that are both catabolic and anabolic are amphibolic.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Anaerobic respiration involves the use of molecules other than oxygen as the final electron (acceptor/donor) in an electron transport chain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Waste products such as sulfur are produced by (oxygenic/anoxygenic/aerobic) photosynthetic bacteria as they obtain electrons for noncyclic photophosphorylation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Another term for a protein catalyst is a(n) (enzyme/ribozyme).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Essential amino acids are amino acids that cannot be synthesized by an organism and so must be provided as nutrients.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Isomerases catalyze reactions in which
A) biomolecules are broken down into their component parts.
B) groups are transferred from one molecule to another.
C) biomolecules are oxidized or reduced.
D) atoms in biomolecules are rearranged.
E) biomolecules are assembled from smaller molecules.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Light energy is used to fuel the assembly of carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the process known as
A) oxidation.
B) fermentation.
C) chemiosmosis.
D) photosynthesis.
E) gluconeogenesis.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The pentose phosphate pathway generates all the necessary precursors for nucleotide biosynthesis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
When a noncompetitive inhibitor molecule binds to an (active/allosteric) site on an enzyme, the shape of the active site changes so that the substrate molecules can no longer bind.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During reactions catalyzed by oxidoreductases an electron donor is
A) reduced.
B) degraded.
C) synthesized.
D) unaltered.
E) oxidized.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 77
Related Exams