A) less than 1.
B) equal to 1.
C) greater than 1.
D) dependent on mass m.
E) impossible to determine.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cable lifting a 4.00-lb bowling ball stretches by 3.00 mm. If the cable is cut in half and both halves are used together to lift the same bowling ball, each cable will stretch by
A) 0.50 mm.
B) 0.75 mm.
C) 1.00 mm.
D) 1.25 mm
E) 1.50 mm.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shows force exerted by two springs with spring constants and , respectively, as a function of extension/compression. Which of the following statements is not true? 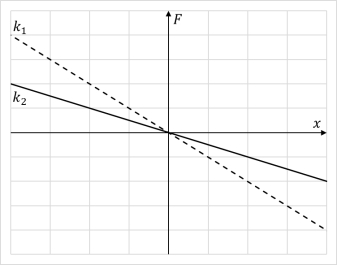
A) At the same extension force exerted by spring one is larger than force exerted by spring two
B) When the force exerted by spring one is the same as force exerted by spring two, the latter is extended more.
C) If both springs have the same dimensions, spring one is made from a stiffer material than spring two.
D) If the springs are made of the same material and have the same length, spring one has a smaller cross-sectional area than spring two.
E) If the springs are made of the same material and have the same cross-sectional areas, spring one is shorter than spring two.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cube expands by 6.94 mm3 when moved from normal conditions to a vacuum chamber. If the bulk modulus of the material is 28.5 GPa, what is the length of the side of that cube?
A) 1.95 mm
B) 0.125 m
C) 4.42 cm
D) 12.5 m
E) 1.95 km
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Young's modulus depends on the geometric shape of the object:
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.83 m-long aluminum "singing" rod is vertically balanced on the floor on one of its ends. Calculate the pressure on the ground exerted by the road due to the weight of the road. The density of Al is QUOTE 2.70×103 kg/m3 and the diameter of the rod is 1.27 cm.
A) 2.7 N/m2
B) 8.4 N/m2
C) 2.7×104 N/m2
D) 4.8×104 N/m2
E) 4.94×103 N/m2
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A wire has a diameter of 0.75 mm. It is stretched 0.20% of its original length when a mass of 5.0 kg is hanging from it. What is the Young's modulus of the wire?
A) 1.4 x 1010 N/m2
B) 5.6 x 1010 N/m2
C) 1.7 x 1011 N/m2
D) 5.6 x 108 N/m2
E) 1.4 x 108 N/m2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
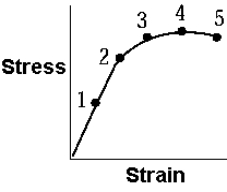 The point that identifies the fracture point of the material whose graph of stress as a function of strain is shown is
The point that identifies the fracture point of the material whose graph of stress as a function of strain is shown is
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
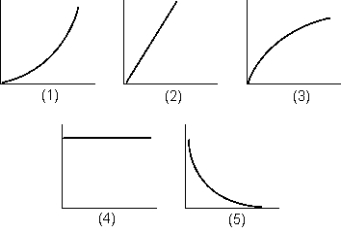 If you measure the magnitude of the force required to stretch a typical laboratory spring as a function of the MAGNITUDE of stretch, which of the graphs shown would best represent your data?
If you measure the magnitude of the force required to stretch a typical laboratory spring as a function of the MAGNITUDE of stretch, which of the graphs shown would best represent your data?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A college student measures his height just before he goes to bed at night and also right after he gets up in the morning the next day. His measurements are 1.80 m, and 1.82 m, respectively. What is the compressive strain on his body due to the normal force and the gravity that are acting on him all day long?
A) 2/182
B) 2/180
C) 1.82 m-1.80 m
D) 182/180
E) 180/182
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fill In the blank. If you double the radius of a steel cable without changing its length, you would __________ its elastic constant.
A) double
B) triple
C) quadruple
D) halve
E) not change
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A spring is made of a wire of radius r and length L. If the radius of the wire and the length of the wire were doubled, the spring constant of the spring would
A) double.
B) quadruple.
C) halve.
D) quarter.
E) remain unchanged.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
True or false? Volume stress is equal to the pressure on the object.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fill in the blank. If you double the cross-sectional area of a steel rod, you would __________ the Young's modulus of steel.
A) double
B) triple
C) quadruple
D) cut in half
E) not change
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you grab each end of a pencil and try to pull the ends apart, you are putting the pencil under tension or tensile stress; if you push the ends toward each other, you are putting the pencil under
A) volume stress.
B) compressive stress.
C) shear stress.
D) Both A and B are correct.
E) Only C is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bulk modulus of mercury is If a drop of benzene with a volume is moved from a vacuum chamber to a high-pressure chamber with , the volume of the droplet
A) increases by 1.14× 10-4 mm3 .
B) increases by 1.14× 10-7 mm3 .
C) doesn't change.
D) decreases by 1.14× 10-4 mm3 .
E) decreases by 1.14× 10-7 mm3 .
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An 800-kg mass is hung from a 1.50-m copper wire with a cross-sectional area of 0.350 cm2. Young's modulus for copper is 1.10 x 1011 N/m2. How much does the wire stretch?
A) 2.56 mm
B) 2.97 mm
C) 3.14 mm
D) 3.86 mm
E) 4.13 mm
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All elastic materials obey Hooke's law in the region of small strain.
A) True
B) False
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When you squeeze a small stress-ball on all sides in your palm you decrease its volume to ¾ of its original volume. What is the volume strain on the ball?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows ultimate tensile strengths ) and Young's moduli ) for tungsten W) and silicon Si) . Based on the information in the table, what is the ratio of ultimate tensile strains for these materials, namely . 
A) 0.0980
B) 10.2
C) 0.0459
D) 2.77
E) 0.457
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 49
Related Exams