B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about members of the Kingdom Plantae is FALSE?
A) They synthesize organic molecules.
B) They use organic carbon sources.
C) They are multicellular.
D) They undergo photosynthesis.
E) They are composed of eukaryotic cells.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Pure cultures of the same species are not always identical in all ways.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You discovered a unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and peptidoglycan. You suspect the organism is in the group
A) Animalia.
B) Fungi.
C) Plantae.
D) Archaea.
E) Bacteria.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best evidence for a three-domain system?
A) There are three distinctly different Gram reactions.
B) There are three distinctly different sets of metabolic reactions.
C) Nucleotide sequences in ribosomal RNA vary between all three domains.
D) Some bacteria live in extreme environments.
E) There are three distinctly different types of nuclei.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phylogenetic classification of bacteria is based on
A) cell morphology.
B) Gram reaction.
C) habitat.
D) diseases.
E) rRNA sequences.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the most popular taxonomic tools is DNA fingerprinting to develop profiles of organisms. These profiles provide direct information about
A) antigenic composition.
B) protein composition.
C) the presence of specific genes.
D) the similarities between nucleotide sequences.
E) enzymatic activities.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is a reason for NOT classifying viruses in one of the three domains of life (Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya) rather than in a fourth separate domain?
A) Viruses direct anabolic pathways of host cells.
B) Viruses are not composed of cells.
C) Some viruses can incorporate their genome into a hostʹs genome.
D) Viruses are obligate parasites.
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Serological testing is used for screening bacterial isolates for similarities.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10.3 This figure shows the results of a gel electrophoresis separation of restriction fragments of the DNA of different organisms.
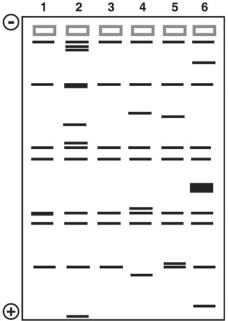 In Figure 10.3, which two are most closely related?
In Figure 10.3, which two are most closely related?
A) 2 and 5
B) 4 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 1 and 3
E) 3 and 5
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following provides taxonomic information that includes the information obtained in the others listed?
A) nucleic acid hybridization
B) nucleic acid-base composition
C) cladogram
D) biochemical tests
E) amino acid sequencing
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Into which group would you place a unicellular organism that has 70S ribosomes and a peptidoglycan cell wall?
A) Animalia
B) Plantae
C) Bacteria
D) Fungi
E) Protist
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Serological testing is based on the fact that
A) the human body makes antibodies against bacteria.
B) antibodies react specifically with an antigen.
C) bacteria clump together when mixed with any antibodies.
D) antibodies cause the formation of antigens.
E) all bacteria have the same antigens.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A biochemical test, in the microbiology world, is used to determine
A) staining characteristics.
B) amino acid sequences of enzymes.
C) capability of a microbe to perform a specific enzymatic activity.
D) nucleic acid-base composition of DNA sequences.
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the outstanding characteristic of the Kingdom Fungi?
A) Members absorb dissolved inorganic matter.
B) Members absorb dissolved organic matter.
C) All members are microscopic.
D) All members are photosynthetic.
E) All members are macroscopic.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As molecular techniques improve, scientists are finding it necessary to reclassify some genera.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characterizes the Domain Bacteria?
A) prokaryotic cells; ester linkages in phospholipids
B) prokaryotic cells; ether linkages in phospholipids
C) complex cellular structures
D) eukaryotic cells; ester linkages in phospholipids
E) multicellular
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A genus can best be defined as
A) a taxon composed of one or more species and a classification level lying below family.
B) the most specific taxon.
C) a taxon belonging to a species.
D) a taxon composed of families.
E) a taxon comprised of classes.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
Figure 10.5
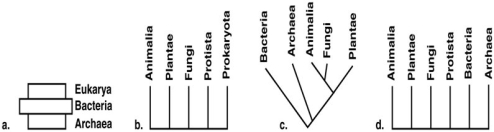 Choose one of the phylogenetic schemes in Figure 10.5 and explain why you feel it is preferable to the others.
Choose one of the phylogenetic schemes in Figure 10.5 and explain why you feel it is preferable to the others.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bacteria and Archaea are similar in which of the following?
A) sensitivity to antibiotics
B) peptidoglycan cell walls
C) plasma membrane ester linkage
D) considered prokaryotic cells
E) methionine as the start signal for protein synthesis
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 58
Related Exams