A) the opportunity cost of production.
B) whether or not a good will sell.
C) the competition in the market.
D) the availability of substitute goods.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium price is sometimes called the:
A) market-clearing price.
B) optimum price.
C) maximum price.
D) quantity-clearing price.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The four important characteristics that define a perfectly competitive market are:
A) a standardized good, full information, no transaction costs, and price-taking participants.
B) standardized information, a finished good, no transaction costs, and price-making participants.
C) a standardized good, the same information for buyers and sellers, low transaction costs, and price-taking participants.
D) a standardized good, full information, no transaction costs, and price-making participants.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the price of gasoline has recently increased. How will this affect the market for hybrid cars?
A) The demand for hybrid cars will increase, increasing the equilibrium price and quantity of hybrid cars.
B) The supply of hybrid cars will increase, decreasing the equilibrium price and increasing the equilibrium quantity of hybrid cars.
C) The demand for hybrid cars will increase, decreasing the equilibrium price and increasing the equilibrium quantity of hybrid cars.
D) The demand for and supply of hybrid cars will increase, decreasing the equilibrium quantity, but the effect on price cannot be determined without more information.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a supply curve?
A) A graphical representation that visually displays the supply schedule.
B) A graph depicting various price-quantity combinations of multiple goods.
C) A graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will sell at one price.
D) A table that displays various price-quantity combinations of a good or service.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a market that is in equilibrium. If the market experiences a decrease in demand:
A) the equilibrium price and quantity will rise.
B) the equilibrium price will rise and the equilibrium quantity will fall.
C) the equilibrium price and quantity will fall.
D) the equilibrium price will fall and the equilibrium quantity will rise.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the demand for socks has decreased. This change can be shown graphically as a:
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
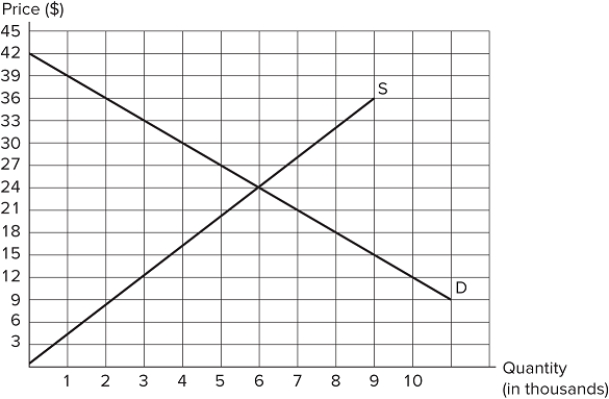 The graph shown depicts the market for a good. Suppose the government sets the price of this good at $36. At this price, there is:
The graph shown depicts the market for a good. Suppose the government sets the price of this good at $36. At this price, there is:
A) a surplus (excess supply) of 9,000 units.
B) a shortage (excess demand) of 2,000 units.
C) a shortage (excess demand) of 7,000 units.
D) a surplus (excess supply) of 7,000 units.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A non-price determinant of supply refers to something:
A) other than supply that affects the price.
B) other than the price that affects supply.
C) that determines how large a role the price plays in the supply decision.
D) that determines how the price is affected by the seller's income.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand schedule assumes that factors other than price:
A) remain the same.
B) must also be in the table.
C) remain separate in the table.
D) change as price changes.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in a non-price factor of demand will cause:
A) a movement along the demand curve.
B) a shift of the demand curve.
C) the demand curve to rotate inward.
D) the demand curve to rotate outward.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the market for roses, which is currently in equilibrium. However, Valentine's Day is coming up, and the rose is the most popular flower to gift to a significant other on this holiday. How will the market for roses change on Valentine's Day?
A) The equilibrium price and quantity will increase due to an increase in supply.
B) The equilibrium price and quantity will increase due to an increase in demand.
C) The quantity demanded will increase because the price increases.
D) The quantity supplied will decrease because the price decreases.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
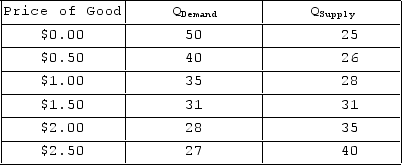 The table shown depicts the demand and supply schedules of a good. At a price of $1.00:
The table shown depicts the demand and supply schedules of a good. At a price of $1.00:
A) a shortage (excess demand) will exist.
B) a surplus (excess supply) will exist.
C) more is being supplied than demanded.
D) the market is in equilibrium.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is the market for used cars not considered to be perfectly competitive?
A) There is complete information.
B) The buyers are not price takers.
C) The good is standardized.
D) There are always very low transaction costs.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
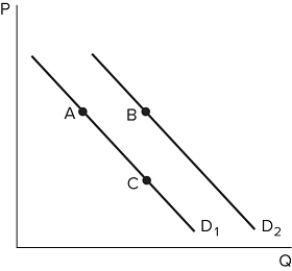 Suppose the graph shown depicts the demand for a normal good. A shift from A to B might be caused by:
Suppose the graph shown depicts the demand for a normal good. A shift from A to B might be caused by:
A) a decrease in the price of a substitute.
B) a decrease in the price of a complement.
C) an increase in the price of a complement.
D) an increase in the good's price.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bob just got laid off from his job and now has no income. What can we assume about his demand?
A) His demand for normal goods will increase.
B) His demand for inferior goods will increase.
C) His demand for inferior goods will decrease.
D) His demand for normal goods will stay the same.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in the price of spaghetti noodles is likely to cause a(n) _____ in the demand for penne pasta, due to a change in the price of a _____.
A) increase; complementary good
B) increase; substitute good
C) decrease; complementary good
D) decrease; substitute good
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve is a(n) _____ line that reflects the _____ relationship between price and quantity.
A) downward-sloping; inverse
B) upward-sloping; inverse
C) downward-sloping; positive
D) upward-sloping; direct
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve is a(n) _____ line that reflects the _____ relationship between price and quantity supplied.
A) downward-sloping; inverse
B) upward-sloping; inverse
C) downward-sloping; direct
D) upward-sloping; direct
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Supply describes how much of something producers:
A) are willing and able to buy under certain circumstances.
B) want to sell under certain circumstances, although they may not be able to.
C) are willing and able to offer for sale at various prices under given circumstances.
D) are able to sell under certain circumstances, although they may not be willing to.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 170
Related Exams