A) inefficient, meaning the society would not be using all its available resources in their best possible uses.
B) efficient, meaning the society would be using all its available resources in their best possible uses.
C) unobtainable, meaning the society cannot produce that combination of goods.
D) efficient, but not attainable.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a worker in Country A can produce either 25 bananas or 5 tomatoes each year. Country A has 200 workers. Suppose a worker in Country B can produce either 18 bananas or 6 tomatoes each year. Country B has 400 workers. Country B will benefit from trade if the country specializes in _____ because _____
A) bananas; it has a comparative advantage at producing bananas.
B) tomatoes; its opportunity cost of tomatoes is higher than that of Country A.
C) tomatoes; its opportunity cost of tomatoes is lower than that of Country A.
D) bananas; it has an absolute advantage at producing bananas.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When nations trade:
A) only the strongest nation benefits.
B) only the weakest nation benefits.
C) all nations involved can benefit.
D) only one nation benefits, but we cannot identify which without more information.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
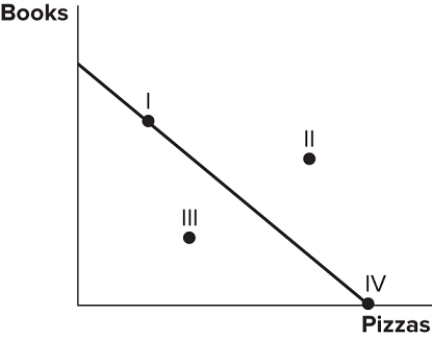 Consider the production possibilities frontier displayed in the figure shown. A society faced with this curve currently:
Consider the production possibilities frontier displayed in the figure shown. A society faced with this curve currently:
A) cannot obtain point II.
B) can only obtain point III.
C) can only obtain point IV or point I.
D) cannot obtain point III.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tom and Jerry have one day to work, but two tasks to focus on: building chairs and tables. If Tom spends all day building chairs, he will make 16 chairs. If he instead devotes his day to building tables, Tom will make 4 tables. If Jerry spends his day building chairs, he will make 14 chairs; if he spends the day building tables, he will make 7 tables. In one day, Tom can produce either:
A) (16 chairs, 4 tables) or (8 chairs, 2 tables) .
B) (8 chairs, 2 tables) or (4 chairs, 6 tables) .
C) (8 chairs, 2 tables) or (4 chairs, 3 tables) .
D) (12 chairs, 3 tables) or (8 chairs, 3 tables) .
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose an American worker can make 20 pairs of shoes or grow 100 apples per day. On the other hand, a Canadian worker can produce 10 pairs of shoes or grow 20 apples per day. The opportunity cost of a pair of shoes is _____ for the United States than Canada, so Canada has a(n) _____ advantage at producing shoes.
A) higher; comparative
B) lower; comparative
C) higher; absolute
D) lower; absolute
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose an American worker can make 20 pairs of shoes or grow 100 apples per day. On the other hand, a Canadian worker can produce 10 pairs of shoes or grow 20 apples per day. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The United States has a comparative advantage at producing shoes.
B) Canada has a comparative advantage at producing shoes.
C) Neither country has a comparative advantage at producing shoes.
D) Both countries have a comparative advantage at producing shoes.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tom and Jerry have one day to work, but two tasks to focus on: building chairs and tables. If Tom spends all day building chairs, he will make 16 chairs. If he instead devotes his day to building tables, Tom will make 4 tables. If Jerry spends his day building chairs, he will make 14 chairs; if he spends the day building tables, he will make 7 tables. In one day, Jerry can produce:
A) 14 chairs and 7 tables.
B) 12 chairs and 6 tables.
C) 10 chairs and 5 tables.
D) 6 chairs and 4 tables.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic theory states that losing a comparative advantage at producing one good means creating a comparative advantage at producing another. As an economy transitions from producing one good to producing another good:
A) those who must transition from the production of one good to the production of another good may find the transition difficult in the short run.
B) the transition can be seen as a success in the short run.
C) outsourcing will always be good for every member of a society.
D) no one will complain in the short run, but in the long run people may not like the transition.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a worker in Country A can make either 10 iPhones or 5 iPads each year. Country A has 100 workers. Suppose a worker in Country B can make either 2 iPhones or 10 iPads each year. Country B has 200 workers. Which of the following is a bundle of goods that Country B could potentially make?
A) (400 iPhones, 2,000 iPads)
B) (300 iPhones, 500 iPads)
C) (200 iPhones, 1,500 iPads)
D) (100 iPhones, 2,000 iPads)
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tom and Jerry have one day to work, but two tasks to focus on: building chairs and tables. If Tom spends all day building chairs, he will make 16 chairs. If he instead devotes his day to building tables, Tom will make 4 tables. If Jerry spends his day building chairs, he will make 14 chairs; if he spends the day building tables, he will make 7 tables. After looking at the production possibilities for both Tom and Jerry, what can we conclude?
A) Tom has a comparative advantage at producing chairs.
B) Jerry has a comparative advantage at producing chairs.
C) Tom has a comparative advantage at producing tables.
D) Neither Tom nor Jerry has a comparative advantage at producing either good.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
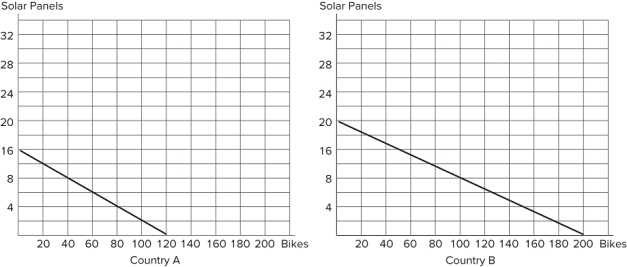 Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. What terms of trade would both countries be willing to agree to?
Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. What terms of trade would both countries be willing to agree to?
A) One solar panel for 2 bikes
B) One solar panel for 7 bikes
C) One solar panel for 8 bikes
D) One solar panel for 12 bikes
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What limits the terms of trade that a country would find acceptable?
A) The country's opportunity costs of production.
B) Whether the country has an absolute advantage at producing a good.
C) How much the country values the good for which it is trading.
D) When the country has a comparative advantage at producing both goods.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose an American worker can make 50 pairs of gloves or grow 300 radishes per day. On the other hand, a Bangladeshi worker can produce 100 pairs of gloves or grow 200 radishes per day. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The U.S. has an absolute advantage at producing both gloves and radishes.
B) The U.S. does not have an absolute advantage at producing either gloves or radishes.
C) The U.S. has an absolute advantage at producing gloves, but not radishes.
D) The U.S. has an absolute advantage at producing radishes, but not gloves.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do people often choose to specialize and trade?
A) It allows them to enjoy more goods than they can create on their own.
B) They can consume a bundle of goods on their production possibilities frontier.
C) It allows them to always produce at a point beyond their own production possibilities frontier.
D) They can take advantage of another nation's poor choices.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A production possibilities frontier is a line or curve that:
A) shows all the possible combinations of outputs that can be produced using all available resources.
B) shows what should be produced when all available resources are efficiently used.
C) shows the best combinations of outputs that can be produced using all available resources.
D) explains why societies make the choices they do.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
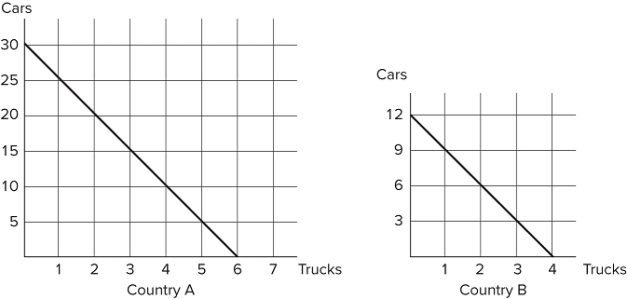 Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. The slope of Country A's production possibilities frontier:
Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. The slope of Country A's production possibilities frontier:
A) measures the opportunity cost of trucks in terms of cars.
B) measures the trade-off that Country A faces when deciding how to allocate resources.
C) is constant, because the opportunity cost remains constant.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of a production possibilities frontier measures:
A) the opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of the other.
B) the trade-off in the consumption of one good versus the other.
C) how much of the resources must be used in order to produce one the goods.
D) the inefficient production of a good.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a worker in Country A can make either 10 iPhones or 5 iPads each year. Country A has 100 workers. Suppose a worker in Country B can make either 2 iPhones or 10 iPads each year. Country B has 200 workers. Which of the following is a bundle of goods that Country B could not make?
A) (400 iPhones, 250 iPads)
B) (300 iPhones, 500 iPads)
C) (200 iPhones, 750 iPads)
D) (100 iPhones, 1,000 iPads)
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tom and Jerry have one day to work, but two tasks to focus on: building chairs and tables. If Tom spends all day building chairs, he will make 16 chairs. If he instead devotes his day to building tables, Tom will make 4 tables. If Jerry spends his day building chairs, he will make 14 chairs; if he spends the day building tables, he will make 7 tables. Because Tom has a _____ opportunity cost for one table compared to Jerry, we know Tom has _____.
A) higher; a comparative advantage at producing tables
B) lower; a comparative advantage at producing tables
C) similar; no advantage at producing either good
D) higher; a comparative advantage at producing chairs
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 154
Related Exams