A) 40
B) 39
C) 42
D) 37
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's total costs are.
A) $20,000.
B) $15,000.
C) $50.
D) $5,000.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Introduction of the Verson Stamping Machine helped firms in the automobile industry
A) eliminate diminishing returns in production.
B) achieve greater economies of scale.
C) reach their minimum efficient scale at a lower level of production.
D) shift their AVC, ATC, and MC curves upward.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
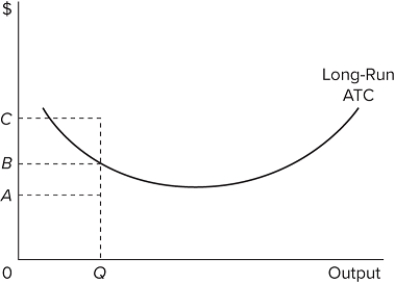 Refer to the diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are
Refer to the diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are
A) unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources.
B) unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology.
C) attainable but imply the inefficient use of resources.
D) attainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic costs are equal to
A) the opportunity costs of all resources owned by the firm.
B) actual expenses paid by the firm for all of its inputs.
C) the sum of all explicit costs and implicit costs.
D) accounting costs.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following output data for a firm. Assume that the amounts of all nonlabor resources are fixed. 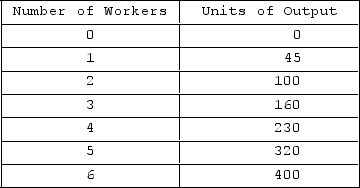 Average product is at a maximum when
Average product is at a maximum when
A) two worker(s) is/are hired.
B) five worker(s) is/are hired.
C) six worker(s) is/are hired.
D) four worker(s) is/are hired.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
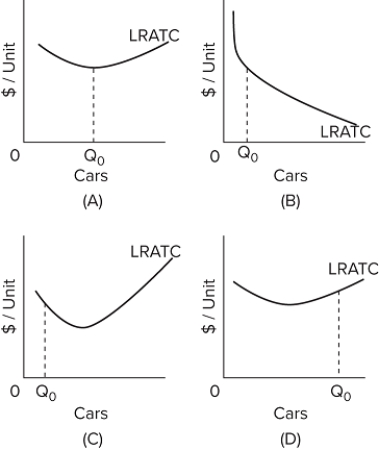 Refer to the provided graphs. They show the long-run average total cost (LRATC) for cars. For which graph are there economies of scale throughout the entire range of output of cars?
Refer to the provided graphs. They show the long-run average total cost (LRATC) for cars. For which graph are there economies of scale throughout the entire range of output of cars?
A) graph A
B) graph B
C) graph C
D) graph D
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harvey quit his job at State University, where he earned $45,000 a year. He figures his entrepreneurial talent or forgone entrepreneurial income to be $5,000 a year. To start the business, he cashed in $100,000 in bonds that earned 10 percent interest annually to buy a software company, Extreme Gaming. In the first year, the firm sold 11,000 units of software at $75 for each unit. Of the $75 per unit, $55 goes for the costs of production, packaging, marketing, employee wages and benefits, and rent on a building.The total revenues of Harvey's firm in the first year were
A) $220,000.
B) $105,000.
C) $605,000.
D) $825,000.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is most likely to be a long-run adjustment for a firm that manufactures cars on an assembly-line basis?
A) an increase in the amount of steel that the firm buys
B) a decrease in the number of production workers in the assembly line
C) a switch in production to a redesigned and retooled facility
D) an increase in the number of shifts of workers from two to three
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data. 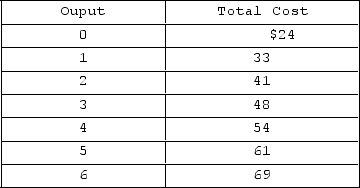 The marginal cost of producing the sixth unit of output is
The marginal cost of producing the sixth unit of output is
A) $12.
B) $8.
C) $24.
D) $45.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm with fixed costs produces at the lowest point on its U-shaped average variable cost curve. If it raises output by 1 unit, then
A) average fixed cost will increase.
B) average total cost will decrease.
C) average fixed cost will necessarily be below average variable cost.
D) average total cost will be less than average variable cost.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows three short-run cost schedules for three plants of different sizes that a firm might build in the long run. 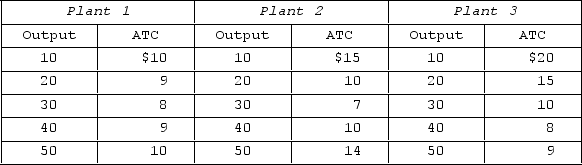 If the three plant sizes shown are the only ones possible, then there are economies of scale in producing
If the three plant sizes shown are the only ones possible, then there are economies of scale in producing
A) up to 10 units of output, and diseconomies of scale after that.
B) up to 20 units of output, and diseconomies of scale after that.
C) up to 30 units of output, and diseconomies of scale after that.
D) up to 40 units of output, and diseconomies of scale after that.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following table shows the relationship between output and costs for two firms in the short run. 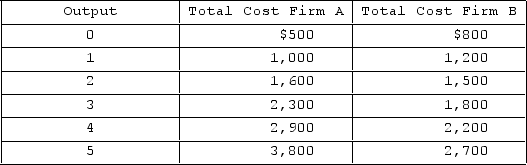 Which of the following is correct?
Which of the following is correct?
A) B has lower fixed costs than A.
B) A has higher per-unit costs than B at an output level of 1.
C) A has greater marginal costs than B at each level of output.
D) B starts experiencing diminishing marginal returns with the second unit of output.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The development of additive manufacturing technology (3-D printers) is expected to lower prices by doing which of the following?
A) reducing the cost of producing blueprints for manufactured goods
B) promoting greater economies of scale in manufacturing
C) reducing the demand for manufactured goods
D) reducing both large fixed set-up costs and transportation costs
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 200 units of output, has average total costs of $250, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are.
A) $20,000.
B) $2.
C) $0.5.
D) $100.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Evaluate this statement: "If the economic profit is zero, a business will shut down. "
Correct Answer

verified
That is an incorrect statement. If a firm is breaking even (that is, earning exactly $0 of economic profit), then its entrepreneurs know they are doing exactly as well as they could expect to do in their best alternative business venture. They are earning enough to cover all their explicit and implicit costs, including the normal profit they could expect to earn in other business ventures. Thus, they have no incentive to change.
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diminishing marginal returns occurs as a firm adds more variable inputs to at least one fixed input because
A) the ability or quality of the variable inputs hired decreases as more of them are hired.
B) the firm must lower the price of its product when it produces more units of output.
C) the per unit cost it must pay for variable inputs increases as more inputs are hired.
D) as more variable inputs are hired, the amount of the fixed input per unit of variable input decreases.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a short-run adjustment?
A) A local bakery hires two additional bakers.
B) Six new firms enter the plastics industry.
C) The number of farms in the United States declines by 5 percent.
D) BMW constructs a new assembly plant in South Carolina.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
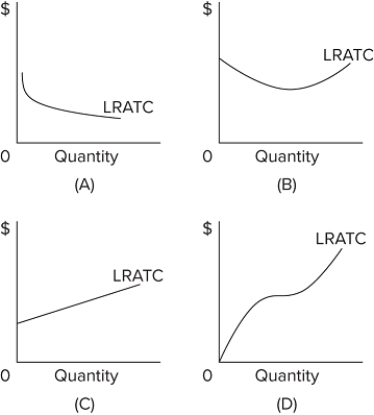 Refer to the provided graphs. They show the long-run average total cost (LRATC) for a product. For which graph would a firm experience first economies and then diseconomies of scale over its range of output?
Refer to the provided graphs. They show the long-run average total cost (LRATC) for a product. For which graph would a firm experience first economies and then diseconomies of scale over its range of output?
A) graph A
B) graph B
C) graph C
D) graph D
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cash expenditures a firm incurs to pay for resources are called
A) implicit costs.
B) explicit costs.
C) normal profit.
D) opportunity costs.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 445
Related Exams