A) Debit Notes Receivable and credit Accounts Receivable for $2,060
B) Debit Accounts Receivable and credit Notes Receivable for $2,000
C) Debit Notes Receivable for $2,000, debit Interest Receivable for $60, credit Accounts Receivable for $2,000, and credit Interest Revenue for $60
D) Debit Notes Receivable and credit Accounts Receivable for $2,000
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company lends $10,000 to an employee who signs a 9%,6-month promissory note. What is the total amount of interest on this note?
A) $900
B) $450
C) $10,450
D) $2,700
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On January 1,a company lends $90,000 to a customer for one year at a 7% annual interest rate.The note requires the payment of interest twice each year on June 30 and December 31.The company records adjusting entries on a monthly basis.At the end of each month in which the company does not receive any interest payments,the company:
A) records an entry with a debit to Cash of $525 and a credit to Interest Revenue of $525.
B) records an entry with a debit to Notes Receivable of $525 and a credit to Cash of $525.
C) records an entry with a debit to Interest Receivable of $525 and a credit to Interest Revenue of $525.
D) does not record an adjusting entry, since no transaction has occurred.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A scenario under which a company's credit sales are increasing and its accounts receivable turnover is decreasing might suggest:
A) channel stuffing.
B) cookie jar accounting.
C) an investment opportunity.
D) improved receivables monitoring.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bad Debt Expense is a:
A) permanent account so its balance carries forward to the next accounting period
B) permanent account so its balance is closed (zeroed out) at the end of the accounting period
C) temporary account so its balance is closed (zeroed out) at the end of the accounting period
D) temporary account so its balance carries forward to the next accounting period
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume ABC sells its receivables to another company for immediate cash on a regular basis.How should the factoring fee be reported in the income statement?
A) Selling expense
B) Non-operating expense
C) Sales returns
D) Not at all
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a note receivable that was created on November 1,2015 and is due for repayment on October 31,2016,what is the time fraction needed to compute interest revenue for the year ended December 31,2015?
A) 2/12
B) 2/10
C) 12/12
D) 22/12
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The receivables turnover ratio is calculated using the total net receivables.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a company did not extend credit to customers:
A) gross revenue would increase.
B) costs would increase but so would sales revenue.
C) costs would decrease but so would sales revenue.
D) gross profit would increase.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harney Inc.uses the percentage of credit sales method of estimating doubtful accounts.The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has an unadjusted credit balance of $2,700 and the company had $140,000 of net credit sales during the period.Harney has experienced bad debt losses of 4% of credit sales in prior periods.After making the adjusting entry for estimated bad debts,what is the ending balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts account?
A) $8,300
B) $5,400
C) $2,900
D) $5,600
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accounts Receivable,Net (or Net Accounts Receivable) equals Accounts Receivable (gross) minus:
A) Cost of Goods Sold.
B) Bad Debt Expense.
C) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
D) Current Liabilities.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Interest on a two-month,7%,$1,000 note would be calculated as $1,000 × 0.07 × 2.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When interest is calculated for periods shorter than a year,the formula to calculate interest is:
A) I = P × R × T, where I = interest calculated, P = principal, R = annual interest rate, and T = number of months.
B) I = P × R × T, where I = interest calculated, P = principal, R = annual interest rate, and T = (number of months ÷ 12) .
C) I = P × R × T, where I = interest calculated, P = principal, R = monthly interest rate, and T = (number of months ÷ 12) .
D) I = (MV - P) /T, where I = interest calculated, MV = maturity value, P = principal and T = number of months.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receivables might be sold ("factored") to:
A) lengthen the time to collect from customers.
B) reduce the receivables turnover ratio.
C) generate cash immediately.
D) generate a gain on sale.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ABC Corp.received a 3month,at 8% per year,$1,500 note receivable on November 1.The adjusting entry on December 31 will include a:
A) debit to Interest Revenue of $20
B) credit to Interest Receivable of $10
C) credit to Interest Revenue of $120
D) credit to Interest Revenue of $20
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
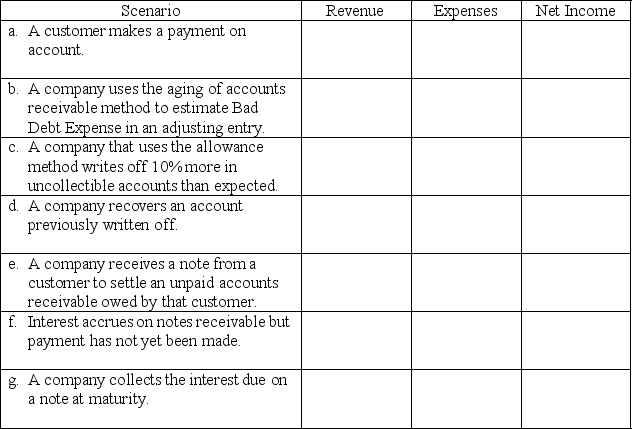
Consider the scenarios listed in the table below.
Required:
For each scenario below,indicate related impact on revenues,expenses,and net income in the current period by answering increase,decrease,or no effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wheeling Inc.uses the aging of accounts receivable method.Its estimate of uncollectible receivables resulting from the aging analysis equals $5,000.At the end of the year,the balance of Accounts Receivable is $100,000 and the unadjusted debit balance of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is $500.Credit sales during the year totaled $150,000.What is the estimated Bad Debt Expense for the current year?
A) $4,500
B) $5,000
C) $5,500
D) $7,000
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If your company factors its accounts receivable,it:
A) will focus its collection activities on only the largest Accounts Receivable balances
B) sells outstanding receivables to another company
C) will use major national credit cards to allow its customers to pay for goods
D) will engage in aggressive hounding of its clients to pay their bills
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kata Company uses the allowance method.On May 1,Kata wrote off a $22,000 customer account balance when it becomes clear that the particular customer will never pay.The journal entry to record the write-off on May 1 would include which of the following?
A) Debit to Bad Debt Expense and credit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
B) Debit to Accounts Receivable and credit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
C) Debit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and credit to Bad Debt Expense
D) Debit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and credit to Accounts Receivable
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things being equal,a company is better off when its receivable turnover ratio:
A) and its days-to-collect measure are both low.
B) is high and its days-to-collect measure is low.
C) and its days-to-collect measure are both high.
D) is low and its days-to-collect measure is high.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 230
Related Exams