A) ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns.
B) club mosses, quillworts, and spike mosses.
C) mosses, hornworts, and liverworts.
D) conifers.
E) charophytes.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a field trip,a student in a marine biology class collects an organism that has differentiated organs,cell walls of cellulose,and chloroplasts with chlorophyll a.Based on this description,the organism could be a brown alga,a red alga,a green alga,a charophyte recently washed into the ocean from a freshwater or brackish water source,or a land plant washed into the ocean.The presence of which of the following features would definitively identify this organism as a land plant?
A) alternation of generations
B) sporopollenin
C) rings of cellulose-synthesizing complexes
D) flagellated sperm
E) embryos
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information that follows to answer the questions below. Big Bend National Park in Texas is mostly Chihuahuan desert,where rainfall averages about 10 inches per year.Yet,it is not uncommon when hiking in this bone-dry desert to encounter mosses and ferns.One such plant is called "flower of stone." It is not a flowering plant,nor does it produce seeds.Under arid conditions,its leaflike structures curl up.However,when it rains,it unfurls its leaves,which form a bright green rosette on the desert floor.Consequently,it is sometimes called the "resurrection plant." At first glance,it could be a fern,a true moss,or a spike moss. -Which of the following features is most important in order for true mosses and ferns to survive and reproduce in the desert?
A) that the sporophytes occupy only permanently shady, north-facing habitats
B) that the sporophytes hug the ground, growing no taller than a couple of inches
C) either that their gametophytes grow close together, or that they be hermaphroditic
D) that the sporophytes have highly lignified vascular tissues
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In plants,which of the following are produced by meiosis?
A) haploid sporophytes
B) haploid gametes
C) diploid gametes
D) haploid spores
E) diploid spores
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most direct ancestors of land plants were probably ________.
A) kelp (brown alga) that formed large beds near the shorelines
B) green algae
C) photosynthesizing prokaryotes (cyanobacteria)
D) liverworts and mosses
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose an efficient conducting system evolved in a moss that could transport water and other materials as high as a tall tree.Which of the following statements about "trees" of such a species would not be true?
A) Fertilization would probably be more difficult.
B) Spore dispersal distances would probably increase.
C) Females could produce only one archegonium.
D) Unless its body parts were strengthened, such a "tree" would probably flop over.
E) Individuals would probably compete more effectively for access to light.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When discovered in peatlands,"bog bodies" tend to be well preserved.The best explanation is that
A) peat moss is a soil conditioner and pads the bodies so they do not break apart.
B) the low temperature, pH, and oxygen level of peatlands slow down/inhibit the decomposition process.
C) peat moss is made up of partially decayed organic matter and animal and plant bodies are organic.
D) the nitrogen fixing bacteria found in peat moss helps preserve the moss and other organisms.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following traits provide supporting evidence that charophyceans are the closest relatives of land plants,with the exception of the fact that
A) both groups have rings of cellulose synthesizing proteins.
B) in both groups, a phragmoplast forms between daughter nuclei of dividing cells.
C) both groups have alternation of generation.
D) both groups contain peroxisome enzymes.
E) the structure of flagellated sperm is similar in both groups.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is true about the genus Sphagnum?
A) It is an economically important liverwort.
B) It grows in extensive mats in grassland areas.
C) It accumulates to form coal and is burned as a fuel.
D) It is an important carbon sink, reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mitotic activity by the apical meristem of a root makes which of the following more possible?
A) increase of the aboveground stem.
B) decreased absorption of mineral nutrients.
C) increased absorption of CO₂.
D) increased number of chloroplasts in roots.
E) effective lateral growth of the stem.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How could you determine if a plant is heterosporous?
A) Male and female reproductive structures are located on separate plants.
B) It has vascular tissue.
C) It has multiple sporangia.
D) Its diploid sporophyte produces spores via meiosis.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the kingdom Plantae is someday expanded to include the charophytes,then the shared derived characteristics of the kingdom will include 1) rings of cellulose-synthesizing complexes. 2) chlorophylls a and b. 3) alternation of generations. 4) cell walls of cellulose. 5) ability to synthesize sporopollenin.
A) 1 and 5
B) 1, 2, and 3
C) 1, 3, and 5
D) 1, 4, and 5
E) 1, 2, 4, and 5
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of seedless vascular plants?
A) Extant seedless vascular plants are larger than the extinct varieties.
B) Whole forests were dominated by large, seedless vascular plants during the Carboniferous period.
C) They produce many spores, which are really the same as seeds.
D) The gametophyte is the dominant generation.
E) Sphagnum is an economically and ecologically important example.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two small,poorly drained lakes lie close to each other in a northern forest.The basins of both lakes are composed of the same geologic substratum.One lake is surrounded by a dense Sphagnum mat; the other is not.Compared to the pond with Sphagnum,the pond lacking the moss mat should have
A) lower numbers of bacteria.
B) reduced rates of decomposition.
C) reduced oxygen content.
D) less-acidic water.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the description below. There are many advantages for plants to living in an aqueous environment.For example,water provides support,the temperature of water fluctuates much less than on land,and external fertilization is facilitated in water.Nevertheless,plants successfully invaded land and diversified. -Which problem with growing on land does not fit with the adaptation to survive dry terrestrial conditions?
A) avoiding dessication - cuticle
B) uptake of carbon dioxide - stomata
C) transport of water - rhizoids
D) reproduction with no water - pollen/seeds
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you are looking for structures that transfer water and nutrients from a bryophyte gametophyte to a bryophyte sporophyte,then on which part of the sporophyte should you focus your attention?
A) spores
B) seta
C) foot
D) sporangium
E) peristome
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given its composition and location,the phragmoplast should be directly involved in the
A) segregation of daughter chromosomes during anaphase.
B) poleward migration of centrosomes during prophase.
C) synthesis of sporopollenin during G₁ and G₂ phases.
D) construction of the cell plate during cytokinesis.
E) reinforcement of the nuclear envelope during S phase.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following information to answer the next few questions.
Researchers decided to test the hypothesis that if the 2-m tall Polytrichum gametophyte-sporophyte plants had acted as a physical buffer,then they would have reduced water's ability to erode the soil and carry away its nitrogen.They began with four equal-sized areas where Polytrichum mosses grew to a height of 2 m above the soil surface.One of the four areas was not modified.In the second area,the mosses were trimmed to a height of 1 m above the soil surface.In the third area,the mosses were trimmed to a height of 0.5 m above the soil surface.In the fourth area,the mosses were trimmed all the way to the ground,leaving only the rhizoids.Water,simulating rainfall,was then added in a controlled fashion to all plots over the course of one year.The figure below presents four graphs that depict potential results of this experiment.
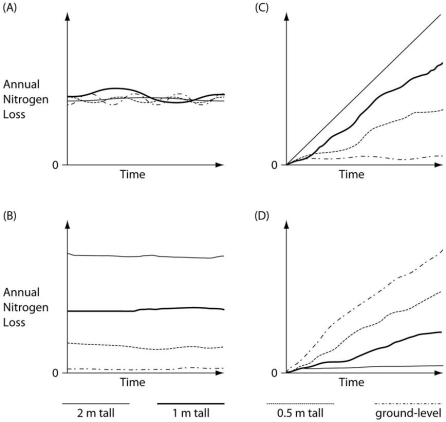 -Which of these potential results of applying a metabolic poison to the rhizoids of Polytrichum should interfere the least with the ability to draw valid conclusions from this experiment?
-Which of these potential results of applying a metabolic poison to the rhizoids of Polytrichum should interfere the least with the ability to draw valid conclusions from this experiment?
A) if, upon dying, the rhizoids leak nitrogenous compounds into the soil before final nitrogen content is measured
B) if, upon dying, decomposition of the rhizoids introduces nitrogenous compounds to the soil before final nitrogen content is measured
C) if the metabolic poison is hydrogen cyanide (HCN) or sodium azide (NaN₃) , and much of the poison remains in the soil
D) if the metabolic poison acts against the mitochondria of the rhizoid cells
E) if the metabolic poison absorbs nitrogen and strongly adheres to soil particles, acting as a sort of glue
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following information to answer the next few questions.
Researchers decided to test the hypothesis that if the 2-m tall Polytrichum gametophyte-sporophyte plants had acted as a physical buffer,then they would have reduced water's ability to erode the soil and carry away its nitrogen.They began with four equal-sized areas where Polytrichum mosses grew to a height of 2 m above the soil surface.One of the four areas was not modified.In the second area,the mosses were trimmed to a height of 1 m above the soil surface.In the third area,the mosses were trimmed to a height of 0.5 m above the soil surface.In the fourth area,the mosses were trimmed all the way to the ground,leaving only the rhizoids.Water,simulating rainfall,was then added in a controlled fashion to all plots over the course of one year.The figure below presents four graphs that depict potential results of this experiment.
 -Why should we expect the soil's nitrogen not to be contained solely within the rhizoids of the Polytrichum mosses?
-Why should we expect the soil's nitrogen not to be contained solely within the rhizoids of the Polytrichum mosses?
A) Rhizoids are associated with fungi that inhibit mineral transfer from soil to rhizoids.
B) Rhizoids are not absorptive structures.
C) Rhizoids consist of single, tubular cells or of filaments of cells.
D) Rhizoids lack direct attachment to the moss sporophytes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information that follows to answer the questions below. Big Bend National Park in Texas is mostly Chihuahuan desert,where rainfall averages about 10 inches per year.Yet,it is not uncommon when hiking in this bone-dry desert to encounter mosses and ferns.One such plant is called "flower of stone." It is not a flowering plant,nor does it produce seeds.Under arid conditions,its leaflike structures curl up.However,when it rains,it unfurls its leaves,which form a bright green rosette on the desert floor.Consequently,it is sometimes called the "resurrection plant." At first glance,it could be a fern,a true moss,or a spike moss. -What feature of both true mosses and ferns makes it most surprising that they can survive for many generations in dry deserts?
A) flagellated sperm
B) lack of vascular tissues
C) lack of true roots
D) lack of cuticle
E) a gametophyte generation that is dominant
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 93
Related Exams