A) increases the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B) increases the domestic interest rate.
C) decreases aggregate expenditures.
D) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
E) increases the equilibrium level of GDP.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left if:
A) there is a significant increase in worker productivity.
B) workers on fixed-wage contracts expect higher inflation.
C) the price of raw materials decreases.
D) the price of capital goods rises.
E) wages fall in anticipation of higher prices.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lower interest rates on business loans usually result in a(n) :
A) decrease in aggregate demand.
B) decrease in aggregate supply.
C) decrease in investment spending.
D) increase in government spending.
E) increase in aggregate expenditures.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long run, increased consumption spending raises only the price level.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The main reason why the short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward is that as the average price level increases, larger scales of production become more profitable.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following explains the effect of prices on profits in the short-run?
A) The direct relationship between aggregate quantity demanded and national output.
B) The direct relationship between aggregate quantity supplied and the price level.
C) The inverse relationship between aggregate quantity demanded and national output.
D) The inverse relationship between aggregate quantity supplied and profits.
E) The inverse relationship between aggregate quantity supplied and national output.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following accounts for a movement along a given AD curve?
A) The substitution effect
B) The tax rate effect
C) The real-balance effect
D) The foreign aid effect
E) The government spending effect
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table given below reports the inflation rate in the U.S. and Canada for two years.
 -Refer to Table 8.1. Assume that the exchange rate is fixed at 1.4 CAD = 1 USD and that price changes for lumber are identical to the inflation rate for each country. If Canadian lumber is sold in year 1 for 5,500 CAD, what is the price of that lumber in year 2, given that exchange rates do not change?
-Refer to Table 8.1. Assume that the exchange rate is fixed at 1.4 CAD = 1 USD and that price changes for lumber are identical to the inflation rate for each country. If Canadian lumber is sold in year 1 for 5,500 CAD, what is the price of that lumber in year 2, given that exchange rates do not change?
A) 5,500 CAD
B) 7,977 CAD
C) 5,698 CAD
D) 7,700 CAD
E) 9,700 CAD
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A lower domestic price level raises aggregate expenditures and, therefore, shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below represents the equilibrium real GDP and price level in the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model.?Figure 8.3
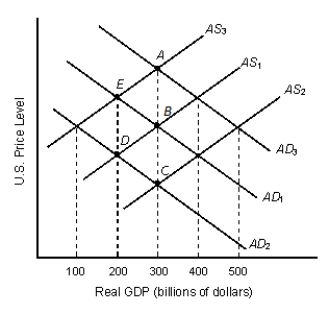 -Refer to Figure 8.3. Potential GDP is greater than real GDP at all output levels:
-Refer to Figure 8.3. Potential GDP is greater than real GDP at all output levels:
A) above $300 billion.
B) between $300 billion and $400 billion.
C) above $400 billion.
D) below $300 billion.
E) above $500 billion.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The intersection of the aggregate demand and the aggregate supply curve defines the equilibrium level of _____ and the price level.
A) real interest rate
B) nominal interest rate
C) nominal GDP
D) real GDP
E) unemployment
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the aggregate supply curve is vertical, then shifts in aggregate demand will not change aggregate output.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pessimistic consumer expectations and decreased government spending are both associated with:
A) a downward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
B) an upward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
C) a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
D) a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
E) a steeper slope of the aggregate demand curve.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The aggregate quantity of goods and services produced will decrease at every price level when resource price rises.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
A) Macroeconomic equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves.
B) The aggregate supply curve indicates a positive relationship between the price level and GDP.
C) Other things equal, a downward shift of the aggregate demand curve implies that the economy is entering a contractionary phase.
D) Aggregate demand and aggregate supply determine the equilibrium price and quantity of any given good.
E) The aggregate demand curve indicates a negative relationship between the price level and GDP.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table given below reports the average hourly wage received by laborers and the price index for two years.?
 -Refer to Table 8.2. The data in the table suggests that in year 2:
-Refer to Table 8.2. The data in the table suggests that in year 2:
A) aggregate supply remains constant.
B) aggregate demand decreases.
C) aggregate supply decreases.
D) aggregate demand increases.
E) aggregate supply increases
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The wealth effect and the interest rate effect are changes in the price level that:
A) bring about a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
B) lead to a shift of the demand curve for a particular good.
C) result in a shift of the aggregate supply curve.
D) help explain the vertical shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
E) cause a movement along the aggregate supply curve.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The fact that the aggregate demand curve slopes downward means that aggregate expenditures increase when the price level decreases.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the correct statement about the aggregate supply curve.
A) The aggregate supply curve is irrelevant for determining macroeconomic equilibrium.
B) The aggregate supply curve shows the various quantities of a particular good that is produced in the economy.
C) The aggregate supply curve shows an inverse relationship between price level and employment.
D) The aggregate supply curve shifts inward with an increase in consumer spending, investment, government spending, and net exports.
E) The aggregate supply curve relates total output in the economy to alternative price levels.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, an increase in aggregate demand will result in:
A) an economic expansion.
B) higher unemployment and a lower equilibrium price level.
C) an economic recession.
D) a decrease in equilibrium real GDP and an increase in the equilibrium price level.
E) a decrease in the overall economic welfare.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 122
Related Exams