A) value added
B) income
C) factor cost
D) expenditure
E) opportunity cost
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To derive net domestic income at market prices from GDP (income approach) ,
A) subtract gross investment from GDP.
B) subtract the statistical discrepancy from GDP.
C) add the statistical discrepancy to GDP.
D) subtract depreciation from GDP.
E) add depreciation to GDP.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is the Human Development Index thought to be a better measure of economic well-being than real GDP per person?
A) It includes a measure of resource depletion.
B) It ignores health, which is hard to measure.
C) It includes leisure time and household production.
D) It includes health and education measures, as well as real GDP per person.
E) It includes only health and education measures, ignoring real GDP per person.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information below to answer the following questions. Fact 20.1.3 The components and robots for Toyota auto assembly lines in Canada are built in Japan. Toyota assembles cars for the Canadian market in Ontario. -Refer to Fact 20.1.3. Choose the correct statement.
A) The assembly line components and robots appear as exports in Canada's GDP.
B) The assembly line components and robots appear as investment in Canada's GDP.
C) The assembly line components and robots appear as a positive entry in calculating Canada's GDP.
D) The assembly line components and robots appear as imports in Canada's GDP.
E) The assembly line components and robots appear as consumption expenditure in Canada's GDP.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What we produce during our working time is ________ as part of GDP and the enjoyment we gain from our leisure time is ________ as part of GDP.
A) included; included
B) not included; not included
C) included; not included
D) not included; included
E) included; sometimes but not always included
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intermediate goods are
A) sold to their ultimate user.
B) produced by one firm, bought by another firm, and used as a component of a final good or service.
C) included directly in the measure of GDP.
D) capital.
E) purchased this year but consumed in future years.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From the following list, choose the item that would be included in a current measure of GDP.
A) the purchase of a previously owned house that was built last year
B) a social security cheque for $500
C) the purchase of 10 litres of gasoline for your car
D) a $2,000 cheque from your Aunt Grace
E) income from the sale of your Canadian Snowfun stocks
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information below to answer the following questions. Fact 20.1.2 Classify each of the following items as a final good or an intermediate good, and identify which is a component of consumption expenditure, investment, or government expenditure on goods and services: Item 1. A DVD bought by a household Item 2. A new airplane bought by WestJet Item 3. Aluminum sheets bought by Boeing Item 4. A new limousine for the prime minister -Refer to Fact 20.1.2. Item 3 is ________ and item 4 is ________.
A) an intermediate good; a final good that is government expenditure
B) a final good that is investment; a final good that is investment
C) a final good that is investment; a final good that is government expenditure
D) an intermediate good; a final good that is investment
E) a final good that is investment; an intermediate good
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The four parts of the business cycle occur in the following order:
A) recession, trough, peak, expansion.
B) expansion, trough, peak, recession.
C) recession, trough, expansion, peak.
D) expansion, trough, recession, peak.
E) trough, peak, expansion, recession.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following relationships is correct?
A) Gross Investment = Net Investment + Depreciation
B) Consumption expenditure = Net Investment - Depreciation
C) Net Investment = Gross Investment + Depreciation
D) Depreciation = Gross Investment - Consumption expenditure
E) Saving = Gross Investment - Taxes
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following question.
Table 20.2.7
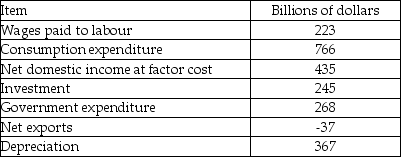 -Table 20.2.7 shows items of income and expenditure in an economy. GDP equals
-Table 20.2.7 shows items of income and expenditure in an economy. GDP equals
A) $1,242 billion.
B) $435 billion.
C) $802 billion.
D) $875 billion.
E) $2,267 billion.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
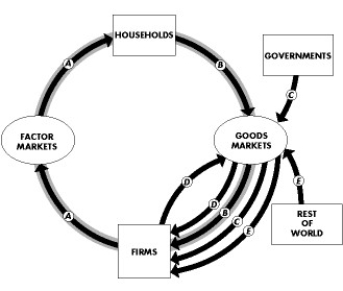 Figure 20.1.1
-Refer to Figure 20.1.1, which shows the circular flow of expenditure and income for Venus. During 2014, A was $100, B was $50, C was $30 and D was $10. How much is net exports?
Figure 20.1.1
-Refer to Figure 20.1.1, which shows the circular flow of expenditure and income for Venus. During 2014, A was $100, B was $50, C was $30 and D was $10. How much is net exports?
A) $10
B) $25
C) $30
D) $50
E) $100
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bakery uses flour to produce bread. When calculating GDP, we include ________, because when we add the value of the flour to the value of the loaf of bread to calculate GDP, the result is ________.
A) only the value of the bread sold in a store; double counting
B) only the value of the flour used to produce the bread; double counting
C) both the value of the bread sold in a store and the value of the flour used to produce the bread; double counting
D) both the value of the bread sold in a store and the value of the flour used to produce the bread; the true value of the economy's output
E) none of the above
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following question.
Table 20.4.2
 -Refer to Table 20.4.2. An economy produces only digital cameras, chocolate bars, and watches. The table gives the quantities produced and prices in 2012 and 2013.
The base year is 2012.
The chained-dollar real GDP in 2013 is
-Refer to Table 20.4.2. An economy produces only digital cameras, chocolate bars, and watches. The table gives the quantities produced and prices in 2012 and 2013.
The base year is 2012.
The chained-dollar real GDP in 2013 is
A) $34.
B) $25.
C) $147.
D) $109.
E) $36.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The business cycle is defined as the
A) regular growth rate of the real GDP.
B) regular fluctuations of real GDP below potential GDP.
C) irregular fluctuations of prices around real GDP.
D) periodic but irregular up-and-down movement of total production and other measures of economic activity.
E) periodic and regular up-and-down movement of total production.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is an income flow from firms to households?
A) goods and services
B) factor services
C) payments for goods and services
D) payments for factor services
E) loans
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of intermediate goods is not counted in GDP
A) to keep from including goods that reduce society's welfare.
B) because of the tremendous difficulty in keeping track of all the intermediate goods produced in an economy as large as Canada.
C) because they are only sold in factor markets.
D) to avoid counting their value twice and overstating the value of GDP.
E) because they are not consumed in the current year.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Potential GDP is
A) the maximum amount of GDP that can be produced while avoiding shortages of labour, capital, land, and entrepreneurship that would bring rising inflation.
B) the same as real GDP.
C) the same as nominal GDP.
D) equal to real GDP multiplied by the price level.
E) equal to nominal GDP multiplied by the price level.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The maximum level of real GDP that can be produced while avoiding shortages of labour, capital, land, and entrepreneurial ability that would bring rising inflation is
A) real GDP.
B) nominal GDP.
C) actual GDP.
D) potential GDP.
E) productive GDP.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stock and bond sales are not included in GDP because they
A) do not occur in the year in which the production represented by them takes place.
B) represent corporate production.
C) represent indebtedness.
D) are not goods and services.
E) are not sold in the country in which they are produced.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 133
Related Exams