A) provide nutrition
B) increase the osmolarity of the blood
C) increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood
D) decrease the osmolarity of the blood
E) reduce blood clotting
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A blood cell undergoes crenation when it is placed in a(n) ________ solution.
A) isotonic
B) hypertonic
C) hypotonic
D) merotonic
E) homotonic
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -What are the three different components that make up the cytoskeleton in all body cells? (Figure 3-3)
A) thick filaments, thin filaments, intermediate filaments
B) microfilaments, microvilli, villi
C) microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
D) thick filaments, thin filaments, microvilli
E) microtubules, macrotubules, tubules
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The watery component of the cytoplasm is called
A) cytosol.
B) protoplasm.
C) extracellular fluid.
D) interstitial fluid.
E) matrix.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of following properties of microtubules is correct?
A) made of myosin
B) made of actin
C) found only in the terminal web
D) another term for microfilaments
E) interact with dynein and kinesin
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electric potential difference across the cell membrane is known as
A) the membrane potential.
B) the membrane difference.
C) the cellular potential.
D) the cellular difference.
E) the plasmalemma potential.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to the extracellular fluid, cytosol contains
A) a higher concentration of potassium ions.
B) a lower concentration of dissolved proteins.
C) almost no glycogen.
D) a higher concentration of amino acids.
E) almost no lipids.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cilia and flagella contain nine pairs of ________ surrounding a central pair.
A) microvilli
B) microfilaments
C) microsomes
D) microtubules
E) intermediate filaments
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nucleus is surrounded by the
A) plasma membrane.
B) membranous sac.
C) phospholipid bilayer.
D) nuclear envelope.
E) chromosome shield.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cytoskeleton components moves the chromosomes during cell division?
A) microfilaments
B) intermediate filaments
C) thick filaments
D) microtubules
E) basal bodies
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is the plasma membrane involved in structural support of body tissues?
A) It has specialized connections to other cells or extracellular materials.
B) It primarily consists of fibrous proteins.
C) It is inflated by cytoplasm at high pressure.
D) Tissues are largely composed of empty plasma membranes left by dead cells.
E) It is hydrophobic, so it repels extracellular fluid and attracts the membranes of other cells.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During mitosis, chromatids separate into daughter chromosomes at the start of
A) prophase.
B) metaphase.
C) interphase.
D) telophase.
E) anaphase.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-1 The Plasma membrane
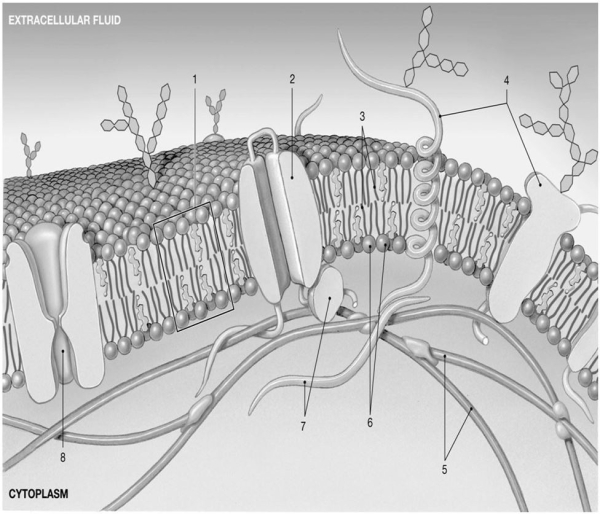 Use Figure 3-1 to answer the following questions.
-What part of the plasma membrane is hydrophobic?
Use Figure 3-1 to answer the following questions.
-What part of the plasma membrane is hydrophobic?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the amount of chloride ion in blood plasma increases, which of the following would initially occur?
A) The blood osmotic pressure will increase.
B) The blood osmotic pressure will decrease.
C) The blood osmotic pressure will stay the same.
D) The blood hydrostatic pressure will increase.
E) The blood hydrostatic pressure will decrease.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diffusion of a substance across the cell membrane may be influenced by all of the following except
A) the availability of ATP.
B) the presence of membrane channels for the substance.
C) its charge of the substance.
D) its concentration gradient.
E) its lipid solubility.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of forming mRNA is called
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) ribolation.
E) auscultation.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of a cell's DNA is located in its
A) ribosomes.
B) lysosomes.
C) Golgi apparatus.
D) nucleus.
E) nucleolus.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cytoplasm contains the fluid cytosol, insoluble inclusions, and the
A) microvilli.
B) nucleolus.
C) enzymes.
D) organelles.
E) cilia.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -How is DNA organized in the nucleus when the cell is prepared for division? How is DNA organized in the nucleus when the cell is not dividing? (Figure 3-11)
A) ______tightly coiled as chromosomes; loosely coiled as chromatin
B) tightly coiled as chromatin; loosely coiled as chromosomes
C) loosely coiled as chromosomes; tightly coiled as chromatin
D) loosely coiled as chromatin; tightly coiled as chromosomes
E) loosely coiled as chromosomes; loosely coiled as chromatin
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________, which is usually inactive in adult cells, is active in 90% of cancer cells.
A) Phagocytosis
B) Apoptosis
C) The p53 gene
D) Telomerase
E) DNA polymerase
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 190
Related Exams