A) excitatory
B) depolarizing
C) temporal
D) saltatory
E) inhibitory
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
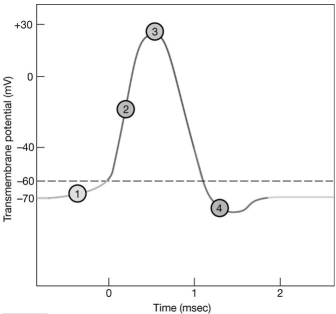 Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-When is the neuron in the refractory period?
Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-When is the neuron in the refractory period?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
IPSPs (inhibitory postsynaptic potentials)
A) are local depolarizations.
B) are local hyperpolarizations.
C) increase membrane permeability to sodium ions.
D) block the efflux of potassium ions.
E) block the efflux of calcium ions.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The part of the peripheral nervous system that carries sensory information to the CNS is designated
A) motor.
B) afferent.
C) efferent.
D) autonomic.
E) somatic.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A postsynaptic neuron will have an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) when
A) chemically regulated potassium channels are open and potassium is diffusing out of the cell.
B) more calcium ions than usual diffuse into the neuron.
C) chemically regulated sodium channels are open and sodium is diffusing into the cell.
D) the neuron is hyperpolarized.
E) more potassium ions than usual diffuse out of the neuron.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurons that have one axon and one dendrite,with the soma in between,are called
A) anaxonic.
B) unipolar.
C) bipolar.
D) tripolar.
E) multipolar.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Puffer fish poison blocks voltage-gated sodium channels like a cork.What effect would this neurotoxin have on the function of neurons?
A) Neurons would depolarize more rapidly.
B) Action potentials would lack a repolarization phase.
C) The absolute refractory period would be shorter than normal.
D) The axon would be unable to generate action potentials.
E) None,because the chemically gated sodium channels would still function.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The site in the neuron where EPSPs and IPSPs are integrated is the
A) chemical synapse.
B) electrical synapse.
C) axon hillock.
D) dendritic membrane.
E) synaptic terminal.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
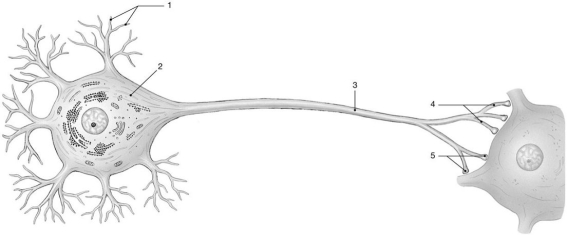 Figure 12-1 The Neuron
Use Figure 12-1 to answer the following questions:
-What is contained inside the structure labeled "5"?
Figure 12-1 The Neuron
Use Figure 12-1 to answer the following questions:
-What is contained inside the structure labeled "5"?
A) neuroglia
B) sodium ions
C) acetylcholinesterase
D) calcium ions
E) neurotransmitter molecules
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when membrane potential approaches the potassium equilibrium potential?
Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when membrane potential approaches the potassium equilibrium potential?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Axons terminate in a series of fine extensions known as
A) telodendria.
B) terminals.
C) collaterals.
D) dendrites.
E) synapses.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ monitor the digestive,respiratory,cardiovascular,urinary,and reproductive systems.
A) Spinal nerves
B) Unipolar neurons
C) Internoceptors
D) Exteroceptors
E) Proprioceptors
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most abundant class of neuron in the central nervous system is
A) anaxonic.
B) bipolar.
C) multipolar.
D) pseudopolar.
E) unipolar.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The minimum stimulus required to trigger an action potential is known as the
A) threshold.
B) all-or-none response.
C) potential.
D) incentive.
E) summation.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deteriorating changes in the distal segment of an axon as a result of a break between it and the soma is called ________ degeneration.
A) neural
B) central
C) peripheral
D) Wallerian
E) conduction
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the chemically gated sodium channels in the postsynaptic membrane were completely blocked,
A) synaptic transmission would fail.
B) release of neurotransmitter would stop.
C) smaller action potentials would result.
D) the presynaptic membrane would be unable to reach threshold.
E) the presynaptic neuron would release a different neurotransmitter.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neuron cell bodies in the PNS are clustered together in masses called
A) fibers.
B) tracts.
C) nerves.
D) nuclei.
E) ganglia.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tiny gaps between adjacent Schwann cells are called
A) neurillema.
B) nodes of Ranvier.
C) axolemma.
D) terminals.
E) vesicles.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Branches that may occur along an axon are called
A) telodendria.
B) synaptic terminals.
C) collaterals.
D) hillocks.
E) synapses.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neuron that receives neurotransmitter from another neuron is called
A) the presynaptic neuron.
B) the motor neuron.
C) an oligodendrocyte.
D) a satellite cell.
E) the postsynaptic neuron.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 168
Related Exams