A) limited to a few industries.
B) limited to specific regions of the country.
C) widely felt outside the United States.
D) confined to the domestic economy.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As disposable income decreases, consumption:
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) may either increase or decrease depending on the mpc.
D) may either increase or decrease depending on the wealth effect.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Keynesian model an expansionary gap will develop if there is:
A) an increase in average labor productivity.
B) too little spending.
C) stabilization policy.
D) too much spending.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run, ______ determines output, and in the long run ______ determines output.
A) potential output; prices
B) potential output; total spending
C) total spending; potential output
D) total spending; prices
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If potential output for an economy equals $5 billion, and actual output equals $4.5 billion, then this economy has a(n) :
A) budget deficit.
B) trade deficit.
C) expansionary gap.
D) recessionary gap.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When aggregate expenditure is given as Y = 400 + 0.5Y, short-run equilibrium output equals:
A) 1,200.
B) 400.
C) 600.
D) 800.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the basic Keynesian model, a tax cut:
A) reduces short-run equilibrium output.
B) increases short-run equilibrium output.
C) reduces potential output.
D) increases potential output.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not describe a characteristic of short-term economic fluctuations?
A) Expansions and recessions are felt in only a few sectors of the economy.
B) Expansions and recessions are irregular in length and severity.
C) The unemployment rate rises during recessions.
D) Durable-goods industries are more sensitive to short-term fluctuations than service and non-durable industries.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A recession occurs when ______, when _______, or when both of these occur.
A) potential output grows slowly; actual output falls below potential output
B) potential output grows slowly; actual output rises above potential output
C) potential output grows rapidly; actual output equals potential output
D) potential output grows rapidly; actual output falls below potential output
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In reference to short-term economic fluctuations, the "peak" refers to:
A) a period in which the economy is growing at a rate significantly above normal.
B) the high point of economic activity prior to a downturn.
C) the high point of economic activity prior to a recovery.
D) a particularly strong and protracted expansion.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run with predetermined prices, when output is less than aggregate expenditure, firms will:
A) reduce production.
B) increase production.
C) increase aggregate expenditure.
D) decrease aggregate expenditure.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is 3 percent frictional unemployment, 4 percent structural unemployment, and -2 percent cyclical unemployment, then the natural rate of unemployment equals:
A) 1%.
B) 2%.
C) 5%.
D) 7%.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The changing age structure of the US population and more efficient labor markets are both possible explanations for:
A) the decline in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the increase in the cyclical rate of unemployment.
C) the 2001 recession.
D) the stagnation of real wages.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The dates of the "official" peaks and troughs of business cycles in the United States are determined by the:
A) Federal Reserve Board.
B) Congressional Budget Office.
C) National Bureau of Economic Research
D) Council of Economic Advisers.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below. 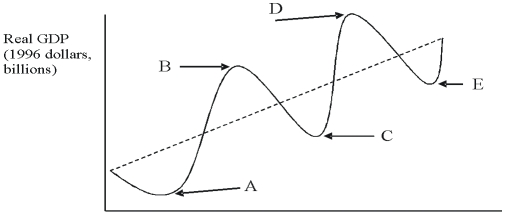 In the figure, a business cycle trough is shown by which point(s) ?
In the figure, a business cycle trough is shown by which point(s) ?
A) A and C and E
B) B and D
C) A only
D) D only
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is 2 percent frictional unemployment, 3 percent structural unemployment, and 1 percent cyclical unemployment, then the natural rate of unemployment equals:
A) 3%.
B) 4%.
C) 5%.
D) 6%.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to occur in the labor market during a recession?
A) The growth rate of real wages declines.
B) Bonuses and promotions become more frequent.
C) New entrants to the labor market have an easier time finding jobs.
D) The supply of labor increases dramatically.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Autonomous expenditure is the portion of aggregate expenditure that:
A) equals aggregate output.
B) equals planned spending.
C) equals induced expenditure.
D) is independent of income.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming that the government can act immediately before the multiplier takes effect, then to offset a reduction in investment by $1 billion, government purchases must be:
A) increased by $1 billion.
B) decreased by $1 billion.
C) increased by $0.5 billion.
D) increased by $2 billion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following data give the dates of successive turning points in U.S. economic activity and the corresponding levels of real GDP at the time. 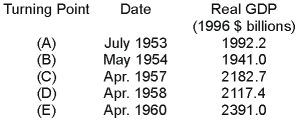 The economy experienced an expansion that lasted from:
The economy experienced an expansion that lasted from:
A) July 1953 to May 1954.
B) May 1954 to April 1957.
C) July 1953 to April 1957.
D) May 1954 to April 1958.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 190
Related Exams