A) there are constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output.
B) there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C) one firm owns a key natural resource.
D) the government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce a particular good or service.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In reality, perfect price discrimination is
A) used by about 75 percent of all monopolies.
B) used by about 50 percent of all monopolies.
C) seldom used by monopolies because it leads to lower profits.
D) rarely possible.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) The competitive firm produces where P = MC.
B) The monopolist produces where P = MC.
C) The competitive firm produces where MR = MC.
D) The monopolist produces where MR = Md.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Perfect price discrimination
A) eliminates deadweight loss.
B) reduces profits to the monopolist.
C) decreases the total quantity sold by the monopolist.
D) requires arbitrage in order for the monopolist to maximize profits.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-10
The monopolist faces the following demand curve:
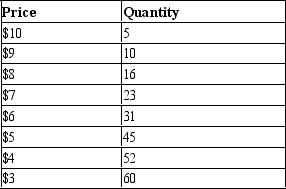 -Refer to Table 15-10. If the monopolist has total fixed costs of $40 and a constant marginal cost of $5, what is the profit-maximizing level of output?
-Refer to Table 15-10. If the monopolist has total fixed costs of $40 and a constant marginal cost of $5, what is the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) 7 units
B) 16 units
C) 23 units
D) 31 units
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist maximizes profits by
A) producing an output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) charging a price equal to marginal revenue and marginal cost.
C) charging a price where marginal cost equals average total cost.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a monopoly market, the socially efficient quantity of output is typically higher than the profit-maximizing quantity of output for the monopolist.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Table 15-22
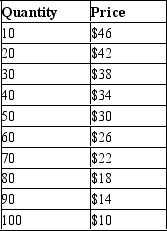 -Refer to Table 15-22. The marginal revenue becomes negative with the production of which unit of output?
-Refer to Table 15-22. The marginal revenue becomes negative with the production of which unit of output?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-21 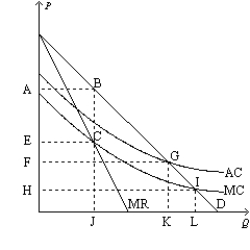 -Refer to Figure 15-21. What is the price and quantity for this natural monopolist under fair return pricing?
-Refer to Figure 15-21. What is the price and quantity for this natural monopolist under fair return pricing?
A) A and J
B) E and J
C) F and K
D) H and L
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist's profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection of which of the following two curves?
A) marginal cost and demand
B) marginal cost and marginal revenue
C) average total cost and marginal revenue
D) average variable cost and average revenue
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist's profit is equal to (Price - Marginal Cost) × Quantity.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some companies merge in order to lower costs through efficient joint production.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-13 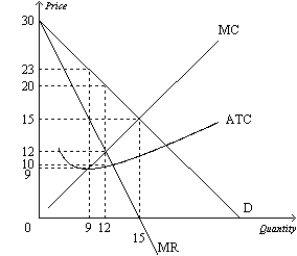 -Refer to Figure 15-13. A profit-maximizing monopolist would create a deadweight loss to society valued at
-Refer to Figure 15-13. A profit-maximizing monopolist would create a deadweight loss to society valued at
A) $12.
B) $24.
C) $42.
D) $84.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly market, total surplus can be defined as the value of the good to
A) producers minus the cost incurred by consumers.
B) producers plus the cost incurred by consumers.
C) consumers minus the costs of producing the good.
D) consumers plus the cost of producing the good.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the preferred strategy for the government to follow to remedy the inefficient allocation of resources associated with monopolies?
A) preventing mergers through antitrust laws
B) regulating the prices that monopolies can charge
C) doing nothing
D) None of the above strategies is preferred. Each is a viable strategy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-8 ![Figure 15-8 -Refer to Figure 15-8. What is the area of deadweight loss? A) the rectangle (A-C) *X B) the triangle 1/2[(A-C) *(Y-X) ] C) the triangle 1/2[(A-B) *(Y-X) ] D) the rectangle (A-C) *X plus the triangle 1/2[(A-C) *(Y-X) ]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2186/11ea6dab_7269_9b17_9009_07cd91284d41_TB2186_00_TB2186_00_TB2186_00_TB2186_00.jpg) -Refer to Figure 15-8. What is the area of deadweight loss?
-Refer to Figure 15-8. What is the area of deadweight loss?
A) the rectangle (A-C) *X
B) the triangle 1/2[(A-C) *(Y-X) ]
C) the triangle 1/2[(A-B) *(Y-X) ]
D) the rectangle (A-C) *X plus the triangle 1/2[(A-C) *(Y-X) ]
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Competitive firms have
A) downward-sloping demand curves, and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
B) downward-sloping demand curves, and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
C) horizontal demand curves, and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
D) horizontal demand curves, and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One problem with government operation of monopolies is that
A) a benevolent government is likely to be interested in generating profits for political gain.
B) monopolies typically have rising average costs.
C) the government typically has little incentive to reduce costs.
D) a government-regulated outcome will increase the profitability of the monopoly.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a firm to price discriminate,
A) it must be a natural monopoly.
B) it must be regulated by the government.
C) it must have some market power.
D) consumers must tell the firm what they are willing to pay for the product.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-8
The following table provides information on the price, quantity, and average total cost for a monopoly.
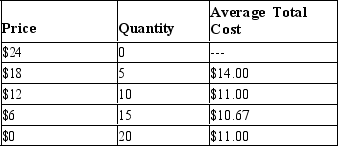 -Refer to Table 15-8. How much extra revenue does the monopolist earn when he lowers the price from $18 to $12?
-Refer to Table 15-8. How much extra revenue does the monopolist earn when he lowers the price from $18 to $12?
A) $10
B) $12
C) $30
D) $41
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 481 - 500 of 637
Related Exams