A) how and for whom to produce.
B) what, how, and for whom to produce.
C) how and for whom to produce but not how much to produce.
D) how much and for whom to produce but not how to produce.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the poor cannot afford proper medical treatment,an economist,for reasons of efficiency,would favor
A) giving the poor added income to spend as they see fit.
B) paying doctors bonuses to treat the poor.
C) paying the medical bills of the poor.
D) giving the poor "medical stamps."
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economy operates efficiently,
A) the MRPs of every input into the production of a good are equal.
B) marginal utility equals marginal cost for every good.
C) the price of a good equals the sum of the marginal physical products of its inputs.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 14-2
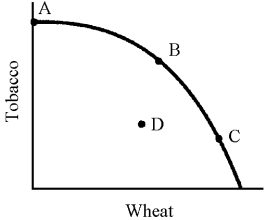 -In Figure 14-2,which movement would represent an improvement for all individuals?
-In Figure 14-2,which movement would represent an improvement for all individuals?
A) A to B
B) C to AC
C) D to B
D) A to D
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government-imposed limits on price movements are likely to
A) increase economic efficiency.
B) decrease economic efficiency.
C) leave economic efficiency unchanged.
D) promote economic growth in the economy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economics can decide
A) the appropriate trade-off between fairness and efficiency.
B) which pricing arrangements are fair and which are unfair.
C) whether a pricing decision will impose heavy inefficiency costs on society.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A factory in a centrally planned economy produces 1,000 left shoes and no right shoes.No corresponding factory produces only right shoes.This outcome is an example of inefficiency in
A) output selection.
B) production planning.
C) product distribution.
D) market segmentation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Price decreases always increase economic efficiency.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price system rations goods among consumers in such a way that
A) all are treated equally.
B) all needs are satisfied.
C) the rich are favored.
D) important needs are satisfied first.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under perfect competition,the market mechanism,without any government regulation,is capable of
A) allocating resources efficiently.
B) solving equity problems.
C) making the average cost of labor equal to the average cost of all commodities.
D) making more income available to the poor.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Central planners in command economies
A) generally set production targets for firms.
B) always consult consumers on the output of goods they want to consume.
C) allow prices to organize the economy's production.
D) depend upon the invisible hand to coordinate economic activities.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Prices set too low can actually be against the public interest.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 14-2
 -As we move down the production possibilities schedule in Figure 14-2,each successive point is
-As we move down the production possibilities schedule in Figure 14-2,each successive point is
A) less efficient.
B) more efficient.
C) equally efficient.
D) more or less efficient; we cannot tell which.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal utility of a gallon of milk to consumers is $2.50 and the MC of producing the gallon of milk is $1.50,then
A) the value of the resources used up in producing one more gallon of milk would be $1 less than the money value of the additional gallon to consumers.
B) society could be made better off by expanding the output of milk.
C) resources are not being used most efficiently.
D) All of the above are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prohibiting price increases in situations of true scarcity could best be described as
A) interfering with the "law" of supply and demand.
B) thwarting the "law" of increasing returns to scale.
C) violating the "law" of increasing cost.
D) interfering with the "law" of diminishing marginal utility.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The task of deciding which consumer gets each of the goods produced in a free-market economy is solved by
A) the price system.
B) the industries which produce the goods.
C) the central planners.
D) citizens with political power.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prices are useful in coordinating society's economic planning because
A) they convey information about which goods are scarce and which are plentiful.
B) economies based on price systems are more flexible than centrally planned economies.
C) economies based on price systems are more likely than centrally planned economies to minimize the cost of producing society's output.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prices
A) solve the problem of distribution of products among consumers.
B) act as rationing devices.
C) under laissez faire produce an efficient allocation of resources.
D) do all of the above.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Command economies are able to achieve greater allocative efficiency than market economies.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a classic administrative snafu,the Army assigns trained classical musicians to kitchen duty and places trained cooks in the military band.This is an example of inefficiency in
A) output selection.
B) production planning.
C) product distribution.
D) market segmentation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 219
Related Exams