A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. A eukaryotic gene has "sticky ends" produced by the restriction endonuclease EcoRI. The gene is added to a mixture containing EcoRI and a bacterial plasmid that carries two genes conferring resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline. The plasmid has one recognition site for EcoRI located in the tetracycline resistance gene. This mixture is incubated for several hours, exposed to DNA ligase, and then added to bacteria growing in nutrient broth. The bacteria are allowed to grow overnight and are streaked on a plate using a technique that produces isolated colonies that are clones of the original. Samples of these colonies are then grown in four different media: nutrient broth plus ampicillin, nutrient broth plus tetracycline, nutrient broth plus ampicillin and tetracycline, and nutrient broth without antibiotics. -Bacteria containing a plasmid into which the eukaryotic gene has integrated would grow
A) in the nutrient broth only.
B) in the nutrient broth and the tetracycline broth only.
C) in the nutrient broth, the ampicillin broth, and the tetracycline broth.
D) in all four types of broth.
E) in the ampicillin broth and the nutrient broth.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To repair a thymine dimer by nucleotide excision repair, in which order do the necessary enzymes act?
A) exonuclease, DNA polymerase III, RNA primase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase
C) DNA ligase, nuclease, helicase
D) DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III, DNA ligase
E) endonuclease, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use Figure 13.3 to answer the following question.
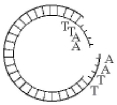 Figure 13.3
-Which enzyme was used to produce the molecule in Figure 13.3?
Figure 13.3
-Which enzyme was used to produce the molecule in Figure 13.3?
A) ligase
B) transcriptase
C) a restriction enzyme
D) RNA polymerase
E) DNA polymerase
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell were unable to produce histone proteins, which of the following would be a likely effect?
A) There would be an increase in the amount of "satellite" DNA produced during centrifugation.
B) The cell's DNA couldn't be packed into its nucleus.
C) Spindle fibers would not form during prophase.
D) Amplification of other genes would compensate for the lack of histones.
E) Pseudogenes would be transcribed to compensate for the decreased protein in the cell.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of histones?
A) Each nucleosome consists of two molecules of histone H1.
B) Histone H1 is not present in the nucleosome bead; instead, it draws the nucleosomes together.
C) The carboxyl end of each histone extends outward from the nucleosome and is called a "histone tail."
D) Histones are found in mammals, but not in other animals or in plants or fungi.
E) The mass of histone in chromatin is approximately nine times the mass of DNA.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reason for using Taq polymerase for PCR is that
A) it is heat stable and can withstand the heating step of PCR.
B) only minute amounts are needed for each cycle of PCR.
C) it binds more readily than other polymerases to the primers.
D) it has regions that are complementary to the primers.
E) it is heat stable, and it binds more readily than other polymerases to the primers.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a linear eukaryotic chromatin sample, which of the following strands is looped into domains by scaffolding?
A) DNA without attached histones
B) DNA with H1 only
C) the 10-nm chromatin fiber
D) the 30-nm chromatin fiber
E) the metaphase chromosome
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes the eukaryotic chromosome?
A) It is composed of DNA alone.
B) The nucleosome is its most basic functional subunit.
C) The number of genes on each chromosome is different in different cell types of an organism.
D) It consists of a single linear molecule of double-stranded DNA plus proteins.
E) Active transcription occurs on heterochromatin but not euchromatin.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After mixing a heat-killed, phosphorescent (light-emitting) strain of bacteria with a living, nonphosphorescent strain, you discover that some of the living cells are now phosphorescent. Which observation(s) would provide the best evidence that the ability to phosphoresce is a heritable trait?
A) DNA passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
B) Protein passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
C) The phosphorescence in the living strain is especially bright.
D) Descendants of the living cells are also phosphorescent.
E) Both DNA and protein passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It became apparent to Watson and Crick after completion of their model that the DNA molecule could carry a vast amount of hereditary information in which of the following?
A) sequence of bases
B) phosphate-sugar backbones
C) complementary pairing of bases
D) side groups of nitrogenous bases
E) different five-carbon sugars
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do histones bind tightly to DNA?
A) Histones are positively charged, and DNA is negatively charged.
B) Histones are negatively charged, and DNA is positively charged.
C) Both histones and DNA are strongly hydrophobic.
D) Histones are covalently linked to the DNA.
E) Histones are highly hydrophobic, and DNA is hydrophilic.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his transformation experiments, what did Griffith observe?
A) Mutant mice were resistant to bacterial infections.
B) Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the pathogenic form.
C) Mixing a heat-killed nonpathogenic strain of bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain nonpathogenic.
D) Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
E) Mice infected with a pathogenic strain of bacteria can spread the infection to other mice.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of DNA polymerase III?
A) to unwind the DNA helix during replication
B) to seal together the broken ends of DNA strands
C) to add nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand
D) to degrade damaged DNA molecules
E) to rejoin the two DNA strands (one new and one old) after replication
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents the order of increasingly higher levels of organization of chromatin?
A) nucleosome, 30-nm chromatin fiber, looped domain
B) looped domain, 30-nm chromatin fiber, nucleosome
C) looped domain, nucleosome, 30-nm chromatin fiber
D) nucleosome, looped domain, 30-nm chromatin fiber
E) 30-nm chromatin fiber, nucleosome, looped domain
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the most logical sequence of steps for splicing foreign DNA into a plasmid and inserting the plasmid into a bacterium? I. Transform bacteria with a recombinant DNA molecule. II. Cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes. III. Extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. IV. Hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA fragments. V. Use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA.
A) I, II, IV, III, V
B) II, III, V, IV, I
C) III, II, IV, V, I
D) III, IV, V, I, II
E) IV, V, I, II, III
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In E. coli, there is a mutation in a gene called dnaB that alters the helicase that normally acts at the origin. Which of the following would you expect as a result of this mutation?
A) No proofreading will occur.
B) No replication fork will be formed.
C) The DNA will supercoil.
D) Replication will occur via RNA polymerase alone.
E) Replication will require a DNA template from another source.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication?
A) It synthesizes RNA nucleotides to make a primer.
B) It catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres.
C) It joins Okazaki fragments together.
D) It unwinds the parental double helix.
E) It stabilizes the unwound parental DNA.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a bacterial cell protect its own DNA from restriction enzymes?
A) by adding methyl groups to adenines and cytosines
B) by using DNA ligase to seal the bacterial DNA into a closed circle
C) by adding histones to protect the double-stranded DNA
D) by forming "sticky ends" of bacterial DNA to prevent the enzyme from attaching
E) by reinforcing the bacterial DNA structure with covalent phosphodiester bonds
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
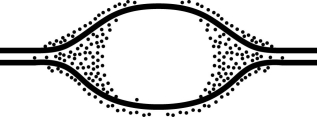 Figure 13.2
-In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (3H thymidine) . After several minutes, the DNA is switched to nonradioactive medium and is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. Figure 13.2 represents the results. It shows a replication bubble, and the dots represent radioactive material. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation of the results?
Figure 13.2
-In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (3H thymidine) . After several minutes, the DNA is switched to nonradioactive medium and is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. Figure 13.2 represents the results. It shows a replication bubble, and the dots represent radioactive material. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation of the results?
A) There are two replication forks going in opposite directions.
B) Thymidine is being added only where the DNA strands are farthest apart.
C) Thymidine is being added only at the very beginning of replication.
D) Replication proceeds in one direction only.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams