A) succinate
B) malate
C) citrate
D) α-ketoglutarate
E) isocitrate
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The complete oxidation of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) to carbon dioxide and water in aerobic respiration consumes how many molecules of oxygen (O₂) ?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 12
E) 36
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis?
A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 10%
D) 38%
E) 100%
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
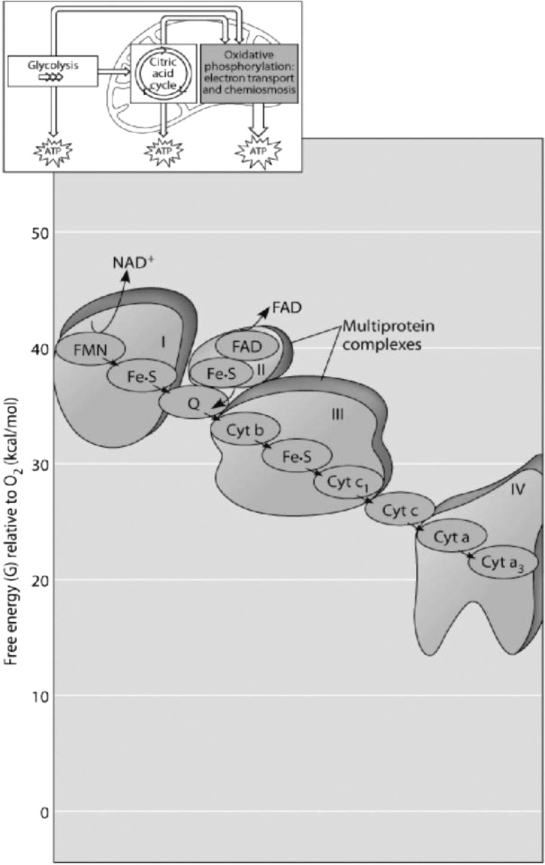 Figure 7.2
-What happens at the end of the chain in Figure 7.2?
Figure 7.2
-What happens at the end of the chain in Figure 7.2?
A) Two electrons combine with a proton and a molecule of NAD+.
B) Two electrons combine with a molecule of oxygen and two hydrogen atoms.
C) Four electrons combine with a molecule of oxygen and four protons.
D) Four electrons combine with four hydrogen and two oxygen atoms.
E) One electron combines with a molecule of oxygen and a hydrogen atom.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
A) an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
B) an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
C) an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
D) an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+
E) an agent that blocks the passage of electrons along the electron transport chain
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated by the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, if glucose is the sole energy source?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) all of it
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yeast cells grown anaerobically can obtain energy by fermentation, which results in the production of
A) ATP, NADH, and pyruvate.
B) ATP and lactate.
C) ATP, CO₂, and lactate.
D) ATP, CO₂, and ethanol.
E) ATP, CO₂, and acetyl CoA.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following produces the most ATP when glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water?
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) citric acid cycle
E) oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which metabolic pathway requires a proton gradient?
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis
E) fermentation
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an electron is transferred to a more electronegative atom
A) it loses potential energy.
B) it gains potential energy.
C) it gains kinetic energy.
D) it oxidizes the more electronegative atom.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ATP made during fermentation is generated by which of the following?
A) the electron transport chain
B) substrate-level phosphorylation
C) chemiosmosis
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) aerobic respiration
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria, which of the following changes occurs?
A) The pH of the matrix increases.
B) ATP synthase pumps protons by active transport.
C) The electrons gain free energy.
D) NAD+ is oxidized.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
A) It increases the surface area for glycolysis.
B) It increases the surface area for the citric acid cycle.
C) It increases the surface area for oxidative phosphorylation.
D) It increases the surface area for substrate-level phosphorylation.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 7.2
-Which of the protein complexes labeled with Roman numerals in Figure 7.2 will transfer electrons to O₂?
Figure 7.2
-Which of the protein complexes labeled with Roman numerals in Figure 7.2 will transfer electrons to O₂?
A) complex I
B) complex II
C) complex III
D) complex IV
E) All of the complexes can transfer electrons to O₂.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an individual is exercising heavily and the muscle becomes oxygen-deprived, muscle cells convert pyruvate to lactate. What happens to the lactate in skeletal muscle cells?
A) It is reduced and converted back to pyruvate in muscle cells.
B) It is oxidized to CO₂ and water.
C) It is taken to the liver and converted back to pyruvate.
D) It oxidizes FADH₂ to FAD+.
E) It is converted to alcohol.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is the
A) oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds.
B) flow of electrons down the electron transport chain.
C) H+ concentration gradient across the membrane holding ATP synthase.
D) transfer of phosphate to ADP.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In alcohol fermentation, NAD+ is regenerated from NADH by
A) oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde.
B) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
C) reduction of pyruvate to lactate.
D) reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol.
E) reduction of acetyl CoA to ethanol.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high-energy foods?
A) They have a lot of oxygen atoms.
B) They have few nitrogen atoms.
C) They have a large number of electrons associated with hydrogen.
D) They have a lot of carbon atoms bound together by single covalent bonds.
E) They are easily reduced.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which catabolic processes may have been used by cells on ancient Earth before free oxygen became available?
A) only glycolysis and fermentation
B) only glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
C) only glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation
D) only oxidative phosphorylation, using an electron acceptor other than oxygen
E) glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, using an electron acceptor other than oxygen
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is
A) the formation of ATP.
B) the reduction of NAD+.
C) a decrease in the pH of the mitochondrial matrix.
D) the creation of a proton-motive force.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 100
Related Exams