A) progresses away from the replication fork.
B) occurs in the 3' → 5' direction.
C) produces Okazaki fragments.
D) depends on the action of DNA polymerase.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the two strands of nucleic acids that make up DNA?
A) The twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands.
B) The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
C) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands.
D) One strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his transformation experiments, what did Griffith observe?
A) Mutant mice were resistant to bacterial infections.
B) Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the pathogenic form.
C) Mixing a heat-killed nonpathogenic strain of bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain nonpathogenic.
D) Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
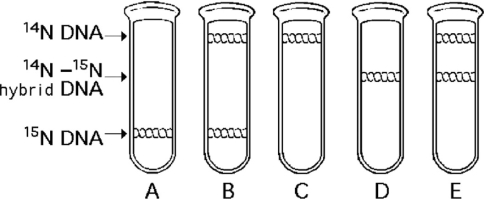 Figure 13.1
-
Figure 13.1
-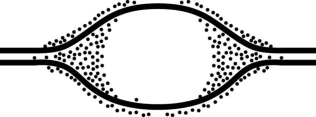 Figure 13.2
In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (3H thymidine) . After several minutes, the DNA is switched to nonradioactive medium and is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. Figure 13.2 represents the results. It shows a replication bubble, and the dots represent radioactive material. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation of the results?
Figure 13.2
In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (3H thymidine) . After several minutes, the DNA is switched to nonradioactive medium and is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. Figure 13.2 represents the results. It shows a replication bubble, and the dots represent radioactive material. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation of the results?
A) There are two replication forks going in opposite directions.
B) Thymidine is being added only where the DNA strands are farthest apart.
C) Thymidine is being added only at the very beginning of replication.
D) Replication proceeds in one direction only.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After mixing a heat-killed, phosphorescent (light-emitting) strain of bacteria with a living, nonphosphorescent strain, you discover that some of the living cells are now phosphorescent. Which observation(s) would provide the best evidence that the ability to phosphoresce is a heritable trait?
A) DNA passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
B) Protein passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
C) The phosphorescence in the living strain is especially bright.
D) Descendants of the living cells are also phosphorescent.
E) Both DNA and protein passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell were unable to produce histone proteins, which of the following would be a likely effect?
A) The cell's DNA couldn't be packed into its nucleus.
B) Spindle fibers would not form during prophase.
C) Expression of other genes would compensate for the lack of histones.
D) DNA polymerase I would not function properly.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a DNA strand in the 5' → 3' direction?
A) primase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA polymerase III
D) topoisomerase
E) helicase
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the basis for the difference in how the leading and lagging strands of DNA molecules are synthesized?
A) DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of a preexisting strand.
B) Helicases and single-strand binding proteins work at the 5' end.
C) The origins of replication occur only at the 5' end.
D) DNA ligase works only in the 3' → 5' direction.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a bacterial cell protect its own DNA from restriction enzymes?
A) by adding methyl groups to adenines and cytosines
B) by using DNA ligase to seal the bacterial DNA into a closed circle
C) by adding histones to protect the double-stranded DNA
D) by forming "sticky ends" of bacterial DNA to prevent the enzyme from attaching
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this sample will be thymine?
A) 8%
B) 16%
C) 31%
D) 42%
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 13.1
-For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned that each nucleotide has only one phosphate and two to five nitrogens. Thus, labeling the nitrogens would provide a stronger signal than labeling the phosphates. Why won't this experiment work?
Figure 13.1
-For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned that each nucleotide has only one phosphate and two to five nitrogens. Thus, labeling the nitrogens would provide a stronger signal than labeling the phosphates. Why won't this experiment work?
A) There is no radioactive isotope of nitrogen.
B) Avery et al. have already concluded that this experiment showed inconclusive results.
C) Although there are more nitrogens in a nucleotide, labeled phosphates actually have 16 extra neutrons; therefore, they are more radioactive.
D) Amino acids (and thus proteins) also have nitrogen atoms; thus, the radioactivity would not distinguish between DNA and proteins.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around
A) polymerase molecules.
B) ribosomes.
C) histones.
D) a thymine dimer.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. A group of six students has taken samples of their own cheek cells, purified the DNA, and used a restriction enzyme known to cut at zero, one, or two sites in a particular gene of interest. -Analysis of the data obtained shows that two students each have two fragments, two students each have three fragments, and two students each have one only. What does this demonstrate?
A) Each pair of students has a different gene for this function.
B) The two students who have two fragments have one restriction site in this region.
C) The two students who have two fragments have two restriction sites within this gene.
D) Each of these students is heterozygous for this gene.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the most logical sequence of steps for splicing foreign DNA into a plasmid and inserting the plasmid into a bacterium?
A) Transform bacteria with a recombinant DNA molecule. Cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes. Hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA fragments. Extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. Use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA.
B) Cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes. Hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA fragments. Use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA. Extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. Transform bacteria with a recombinant DNA molecule.
C) Extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. Cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes. Hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA fragments. Use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA. Transform bacteria with a recombinant DNA molecule.
D) Extract plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. Hydrogen-bond the plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA fragments. Use ligase to seal plasmid DNA to nonplasmid DNA. Transform bacteria with a recombinant DNA molecule. Cut the plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The leading and the lagging strands of DNA formed during DNA replication differ in that
A) the leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
B) the leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end.
C) the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together.
D) the leading strand is synthesized at twice the rate of the lagging strand.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A new DNA strand elongates only in the 5' to 3' direction because
A) DNA polymerase begins adding nucleotides at the 5' end of the template.
B) Okazaki fragments prevent elongation in the 3' to 5' direction.
C) replication must progress toward the replication fork.
D) DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the free 3' end.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 13.1
-Once the pattern found after one round of replication was observed, Meselson and Stahl could be confident of which of the following conclusions?
Figure 13.1
-Once the pattern found after one round of replication was observed, Meselson and Stahl could be confident of which of the following conclusions?
A) Replication is semiconservative.
B) Replication is not dispersive.
C) Replication is not semiconservative.
D) Replication is not conservative.
E) Replication is neither dispersive nor conservative.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During DNA replication, which of the following enzymes covalently connects segments of DNA?
A) helicase
B) DNA polymerase III
C) ligase
D) DNA polymerase I
E) primase
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do histones bind tightly to DNA?
A) Histones are positively charged, and DNA is negatively charged.
B) Histones are negatively charged, and DNA is positively charged.
C) Both histones and DNA are strongly hydrophobic.
D) Histones are covalently linked to the DNA.
E) Histones are highly hydrophobic, and DNA is hydrophilic.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his work with pneumonia-causing bacteria and mice, Griffith found that
A) the protein coat from pathogenic cells was able to transform nonpathogenic cells.
B) heat-killed pathogenic cells caused pneumonia.
C) some substance from pathogenic cells was transferred to nonpathogenic cells, making them pathogenic.
D) the polysaccharide coat of bacteria caused pneumonia.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams