A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) glucose
D) light
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were able to walk into an opening cut into the centre of a large redwood tree, when you exited from the middle of the trunk (stem) outward, you would cross, in order, ________.
A) the annual rings, new xylem, vascular cambium, phloem, and bark
B) the secondary xylem, cork cambium, phloem, and periderm
C) the vascular cambium, oldest xylem, and newest xylem
D) the secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and vascular cambium
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Strawberries have modified horizontal shoots growing along the surface, which are referred to as ________.
A) rhizomes
B) tubers
C) stolons
D) rhizoids
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following arise, directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity?
A) secondary xylem
B) leaves
C) dermal tissue
D) secondary xylem, leaves, dermal tissue, and tubers
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is present in a shoot apical meristem region? I. the region of cell division II. immature buds and leaves III. cells that will give rise to the protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium
A) only I
B) only II
C) only III
D) I, II, and III
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells produced by lateral meristems are known as ________.
A) dermal and ground tissue
B) lateral tissues
C) pith
D) secondary tissues
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is primary growth occurring in an old tree?
A) Closest to ground level at the base of the tree.
B) In young branches where leaves are forming.
C) Where the vascular cambium and cork cambium are located.
D) Nowhere; trees more than a year old have only secondary growth.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following diagram is of a cross-section of a plant leaf. Use the diagram to answer the question. 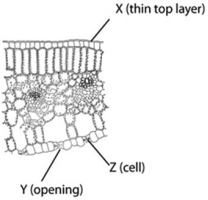 - The main function associated with structure X is ________.
- The main function associated with structure X is ________.
A) absorption of carbon dioxide
B) retention of water
C) collection of light
D) release of carbon dioxide
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct sequence of the zones in the primary growth of a root, moving from the root cap inward?
A) zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of differentiation
B) zone of differentiation, zone of elongation, zone of cell division
C) zone of elongation, zone of cell division, zone of differentiation
D) zone of cell division, zone of differentiation, zone of elongation
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following have unevenly thickened primary walls that support young, growing parts of the plant?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) tracheids and vessel elements
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monocot vascular bundles do not have a vascular cambium between the xylem and phloem. This means that monocots ________.
A) are much less efficient at conducting water and sugars
B) have very thin stems
C) do not produce wood in annual rings
D) cannot produce lateral shoots
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prop roots are the modified aerial adventitious roots of corn that ________.
A) enable the root system to obtain oxygen
B) support tall, top-heavy plants
C) enable the root system to anchor
D) wrap around other plants to support tall, top-heavy plants
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Heartwood and sapwood consist of
A) bark.
B) periderm.
C) secondary xylem.
D) secondary phloem.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing the number of stomata per unit surface area of a leaf when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels decline is most analogous to a human ________.
A) breathing faster as atmospheric carbon dioxide levels increase
B) putting more red blood cells into circulation when atmospheric oxygen levels decline
C) removing red blood cells from circulation when atmospheric oxygen levels increase
D) increasing the volume of its lungs when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels increase
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is a relatively indigestible strengthening polymer that accounts for more than a quarter of the dry mass of wood.
A) Cellulose
B) Starch
C) Lignin
D) None of these choices
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cell types retains the ability to undergo cell division?
A) a parenchyma cell near the root tip
B) a functional sieve tube element
C) a tracheid
D) a stem fibre
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The veins of leaves are ________. I. composed of xylem and phloem II. continuous, with vascular bundles in the stem and roots III. finely branched to be in close contact with photosynthesising cells
A) only I
B) only II
C) only III
D) I, II, and III
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a meristematic region, the cell plate during mitosis is perpendicular to the side of the stem. In what direction will the stem grow?
A) laterally in width
B) vertically in height
C) at a 45-degree angle from the ground
D) away from the sun
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When you eat Brussels sprouts, you are eating ________.
A) immature flowers
B) large axillary buds
C) petioles
D) storage leaves
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What tissue makes up most of the wood of a tree?
A) primary xylem
B) secondary xylem
C) secondary phloem
D) vascular cambium
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 65
Related Exams