A) a way to keep some of our wealth in a readily spendable form for future use.
B) a means of payment.
C) a monetary unit for measuring and comparing the relative values of goods.
D) declared as legal tender by the government.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When we say that money serves as a store of value, we mean that it is:
A) a way to keep some of our wealth in a readily spendable form for future use.
B) a means of payment.
C) a monetary unit for measuring and comparing the relative values of goods.
D) declared as legal tender by the government.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When we say that money serves as a medium of exchange, we mean that it is:
A) a way to keep some of our wealth in a readily spendable form for future use.
B) a means of payment.
C) a monetary unit for measuring and comparing the relative values of goods.
D) declared as legal tender by the government.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information below which shows the demand deposits and actual reserves of a banking system. When the desired reserve ratio is 20 percent, the money creating potential of the entire banking system is: 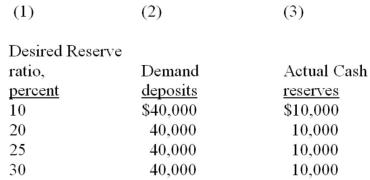
A) $4,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $8,000.
D) $10,000.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the fundamental identity embodied in a balance sheet?
A) Net Worth plus Assets equal Liabilities
B) Assets plus Liabilities equal Net Worth
C) Assets equal Liabilities plus Net Worth
D) Assets plus Reserves equal Net Worth
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Chartered banks increase the supply of money when they purchase either personal IOUs or government bonds from businesses and households.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A basic argument for using the M1 concept of money is that:
A) it includes all of the important financial assets that have any degree of liquidity.
B) the government collects data for the components of M1, but does not do so for M2 and M2+.
C) its components are superior to other financial assets as a store of value.
D) its components are directly and immediately spendable.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Subprime mortgage loans refer to:
A) low-interest rate loans by financial institutions to home buyers with higher-than -average credit risk.
B) high-interest rate loans by financial institutions to home buyers with higher-than -average credit risk.
C) high-interest rate loans by financial institutions to home buyers with no credit risk.
D) high-interest rate loans by financial institutions to home buyers with lower-than -average credit risk.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2011, the value of M2++ in Canada was about:
A) $182 billion.
B) $1092 billion.
C) $233 billion.
D) $2063 billion.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demand deposits are:
A) debts of chartered banks and other financial institutions.
B) debts of the Bank of Canada.
C) credits of the Bank of Canada.
D) credits of chartered banks and other financial institutions.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Money and banking in Canada are federal responsibilities.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bank owns a 10-story office building. In the bank's balance sheet, this would be an example of:
A) an asset.
B) a liability.
C) stock shares.
D) a chequable deposit.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiat money is valuable because:
A) it is backed by gold.
B) it is fractionally backed by gold.
C) it is generally acceptable.
D) it is convertible to gold.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The functions of money are to serve as a:
A) resource allocator, method for accounting, and means of income distribution.
B) unit of account, store of value, and medium of exchange.
C) determinant of consumption, investment, and government spending.
D) factor of production, exchange, and aggregate supply.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the receipts given by goldsmiths to depositors were used to make purchases:
A) the gold standard was created.
B) existing banking laws were violated.
C) the receipts became in effect paper money.
D) a fractional reserve banking system was created.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you write a cheque on a Saskatoon bank to purchase a new Honda Civic, you are employing money as:
A) a medium of exchange.
B) a store of value.
C) a unit of account.
D) all of the above.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume Company X deposits $100,000 in cash in chartered Bank A. If no excess reserves exist at the time this deposit is made and the desired reserve ratio is 20, Bank A can increase the money supply by a maximum of:
A) $50,000.
B) $180,000.
C) $80,000.
D) $500,000.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Coins and paper money are:
A) debts of Chartered banks and savings institutions.
B) debts of the Bank of Canada.
C) credits of the Bank of Canada.
D) credits of chartered banks and savings institutions.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a chartered banking system has $100,000 of outstanding demand deposits and actual cash reserves of $35,000. If the desired reserve ratio is 20 percent, the banking system can expand the supply of money by the maximum amount of:
A) $122,000.
B) $175,000.
C) $300,000.
D) $75,000
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stock market price quotations best exemplify money serving as a:
A) store of value.
B) unit of account.
C) medium of exchange.
D) index of satisfaction.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 286
Related Exams