A) hydrophobic
B) both
C) hydrophilic
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Disulfide bonds stabilize the tertiary structure of a protein.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Upon hydrolysis the dipeptide abbreviated as Gly-Lys will yield the same products as the dipeptide abbreviated as Lys-Gly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Collagen, a protein found in tendons and cartilage, would be classified as a __________ protein.
A) catalytic
B) structural
C) transport
D) storage
E) hormone
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One heavy metal that can cause denaturation of a protein is
A) silver.
B) sodium.
C) barium.
D) iron.
E) calcium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Lead ions disrupt hydrophobic interactions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Proteins that stimulate immune response are known as __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the structural level in each protein. -The protein folds into a compact structure stabilized by interactions between R groups.
A) tertiary
B) quaternary
C) primary structure
D) secondary structure
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Write the zwitterion of glycine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of interaction would you expect between the following R groups in the tertiary structure of a protein? 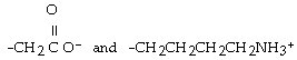
A) disulfide bonds
B) salt bridges
C) hydrogen bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) peptide bonds
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The structural formulas of amino acids are the same EXCEPT for the
A) carboxyl group.
B) alpha carbon.
C) amino group.
D) side (R) group.
E) hydrogen bonding.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the R groups of the following amino acids: cysteine: -CH₂SH; alanine: - 3CH3; serine: -CH₂OH
The name for the dipeptide shown below is __________. 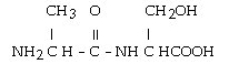
A) alanyl-cysteine
B) alanyl-serine
C) seryl-alanine
D) seryl-cysteine
E) serine-alanine
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a secondary protein structure?
A) dipeptide
B) triglyceride
C) a helix
D) amino acid
E) fatty acid
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The peptide hormone that regulates uterine contractions during labor is __________.
A) oxytocin
B) vasopressin
C) myoglobin
D) an endorphin
E) an enkephalin
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acids and bases denature a protein by disrupting
A) peptide bonds and ionic bonds.
B) amide bonds and alkene bonds
C) hydrophobic interactions and peptide bonds.
D) ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
E) ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The protein that transports oxygen in the blood is __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the structural level in each protein. -the peptide bonds between the amino acids
A) tertiary
B) quaternary
C) primary structure
D) secondary structure
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enkephalins, naturally produced opiates in the body, are found in
A) muscles and bone tissue.
B) brain and kidney tissue.
C) thalamus and spinal cord tissue.
D) heart and lung tissue.
E) pancreas and liver tissue.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which R group would most likely be found in a hydrophobic area of the tertiary structure of a globular protein?
A) -CH?OH
B) - CH?COO-
C) ![]()
D) - CH?CH?CH?CH? H3
E)
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Within hemoglobin, the heme functions as
A) a disulfide bridge.
B) an oxygen carrier.
C) a reducing agent.
D) an α subunit.
E) one of the four protein subunits.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 103
Related Exams