A) outer mitochondrial membrane.
B) matrix and inner mitochondrial membrane.
C) nucleus.
D) cytoplasm.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When did the level of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere become high enough to sustain aerobic respiration?
A) 1.0 billion years ago
B) 3.5 billion years ago
C) 1.5 billion years ago
D) 2.7 billion years ago
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A culture of bacteria growing aerobically is fed glucose containing radioactive carbon and is then examined.During the citric acid cycle,radioactivity would first appear in
A) oxaloacetic acid.
B) CoA.
C) citrate.
D) NADH.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding photosynthesis and cellular respiration is true?
A) Cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts.
B) Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria,and cellular respiration occurs in chloroplasts.
C) Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts.
D) Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts,and cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A kilocalorie is defined as
A) the quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C.
B) the quantity of food used to maintain normal bodily functions.
C) the quantity of food consumed during a given type of exercise.
D) the quantity of glucose needed to increase the body temperature by 1°C.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which step of the citric acid cycle requires both NAD+ and ADP as reactants? 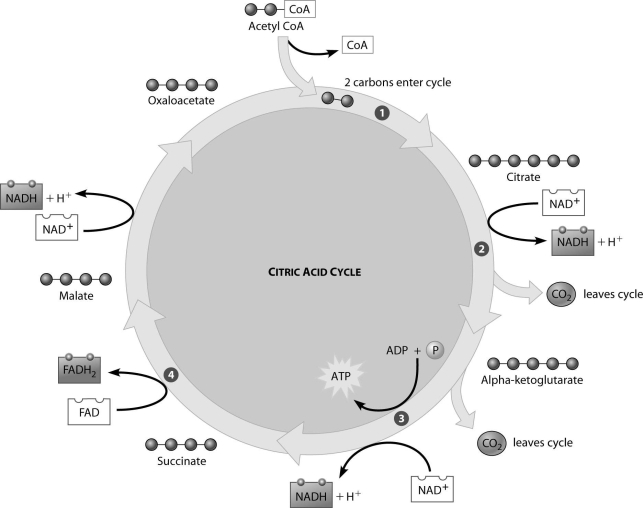
A) step 1
B) step 2
C) step 3
D) step 4
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Humans use about of their daily calories to maintain brain cells and power other life- sustaining activities.
A) 75%
B) 50%
C) 25%
D) 90%
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In fermentation,is .
A) NAD+ ...oxidized
B) NADH ...oxidized
C) NADH ...reduced
D) ethanol ...oxidized
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are products of cellular respiration?
A) energy to make ATP and carbon dioxide
B) oxygen and carbon dioxide
C) oxygen and glucose
D) oxygen and energy to make ATP
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the energy yields from cellular respiration is true?
A) Cellular respiration is more efficient at harnessing energy from glucose than car engines are at harnessing energy from gasoline.
B) The heat produced during cellular respiration is only a tiny fraction of the chemical energy available in a glucose molecule.
C) Cellular respiration converts the kinetic energy of glucose into chemical energy.
D) Cellular respiration converts all of the energy in glucose into high- energy ATP bonds.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A drug is tested in the laboratory and is found to create holes in both mitochondrial membranes.Scientists suspect that the drug will be harmful to human cells because it will inhibit
A) glycolysis.
B) oxidative phosphorylation.
C) the citric acid cycle.
D) the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do cells capture the energy released by cellular respiration?
A) They store it in molecules of carbon dioxide.
B) They produce glucose.
C) The energy is coupled to oxygen.
D) They produce ATP.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In biological systems,an important enzyme involved in the regulation of redox reactions is
A) oxygen.
B) ATP.
C) glucose.
D) dehydrogenase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding food is false?
A) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that consume ATP.
B) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that can produce molecules that are not actually present in the original food.
C) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that make molecules for cellular repair and growth.
D) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that can produce sugar by a process that is the exact opposite of glycolysis.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Respiration _ _,and cellular respiration _.
A) uses glucose ...produces glucose
B) produces glucose ...produces oxygen
C) produces ATP ...is gas exchange
D) is gas exchange ...produces ATP
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During chemiosmosis,
A) energy is released as H+ ions move freely across mitochondrial membranes.
B) a concentration gradient is generated when large numbers of H+ ions are passively transported from the matrix of the mitochondrion to the mitochondrion's intermembrane space.
C) H+ ions serve as the final electron acceptor.
D) ATP is synthesized when H+ ions move through a channel in ATP synthase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding cellular respiration is false?
A) Cellular respiration releases heat.
B) Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide.
C) Cellular respiration produces water.
D) Cellular respiration is a single chemical reaction with just one step.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following options lists the stages in cellular respiration in the correct order?
A) glycolysis,the citric acid cycle,and oxidative phosphorylation
B) the citric acid cycle,oxidative phosphorylation,and glycolysis
C) glycolysis,oxidative phosphorylation,and the citric acid cycle
D) oxidative phosphorylation,glycolysis,and the citric acid cycle
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutant protist is found in which some mitochondria lack an inner mitochondrial membrane.Which of the following pathways would be completely disrupted in these mitochondria?
A) biosynthesis
B) glycolysis
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) alcoholic fermentation
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bacteria that are unable to survive in the presence of oxygen are called
A) facultative anaerobes.
B) obligate anaerobes.
C) aerotolerant anaerobes.
D) obligate aerobes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 66
Related Exams